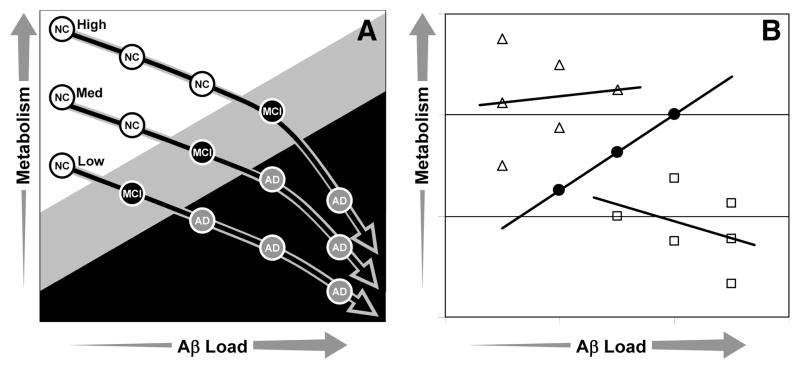
Figure 4.
A, Model of the combined effects of metabolism and Aβ load on cognition. At higher levels of metabolism, more Aβ is required for conversion from normal (white circles) to MCI (black circles) or from MCI to AD (gray circles). Also in this model, Aβ deposition results in decreased metabolism and, at high levels of Aβ, the rate of metabolic inhibition accelerates. B, The hypothetical data from A predicts that correlations between metabolism and Aβ load would be weak in controls (open triangles), strongly positive in MCI (closed circles), and moderately negative in AD (open squares).