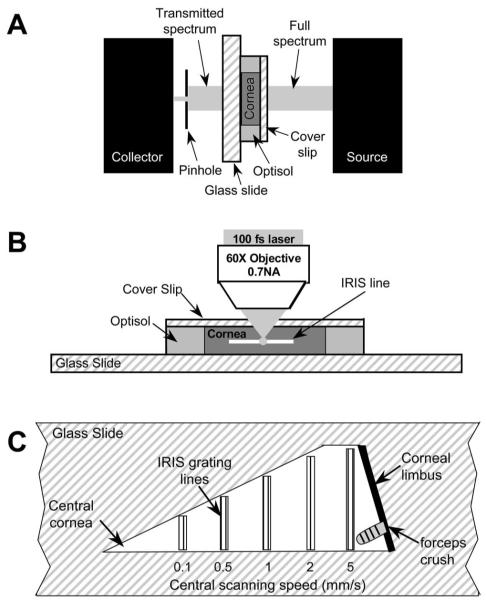
Figure 1.
Experimental setups. (A) System used to measure light transmissivity in living corneal pieces. A full-spectrum (200–1000 nm) beam was emitted from the light source. After it passed through the coverslip, cornea, and glass slide, the transmitted light was then collected and measured by spectrometer. (B) IRIS micromachining apparatus. The live corneal wedges were placed on a glass slide with preservative solution. A thin coverslip was placed over each sample to help keep it flat and the slide-tissue-coverslip assembly was placed on a 3-D computer-controlled scanning stage under a long-working-distance microscope objective with 0.7 NA. (C) IRIS lines micromachined into each corneal piece. One long edge of each corneal piece was aligned with the edge of a glass slide and five sets of lines were micromachined. The two outer lines of each line set were machined at 0.1 mm/s, whereas the central lines were machined at the scanning speeds listed below each set.