Fig. 1.
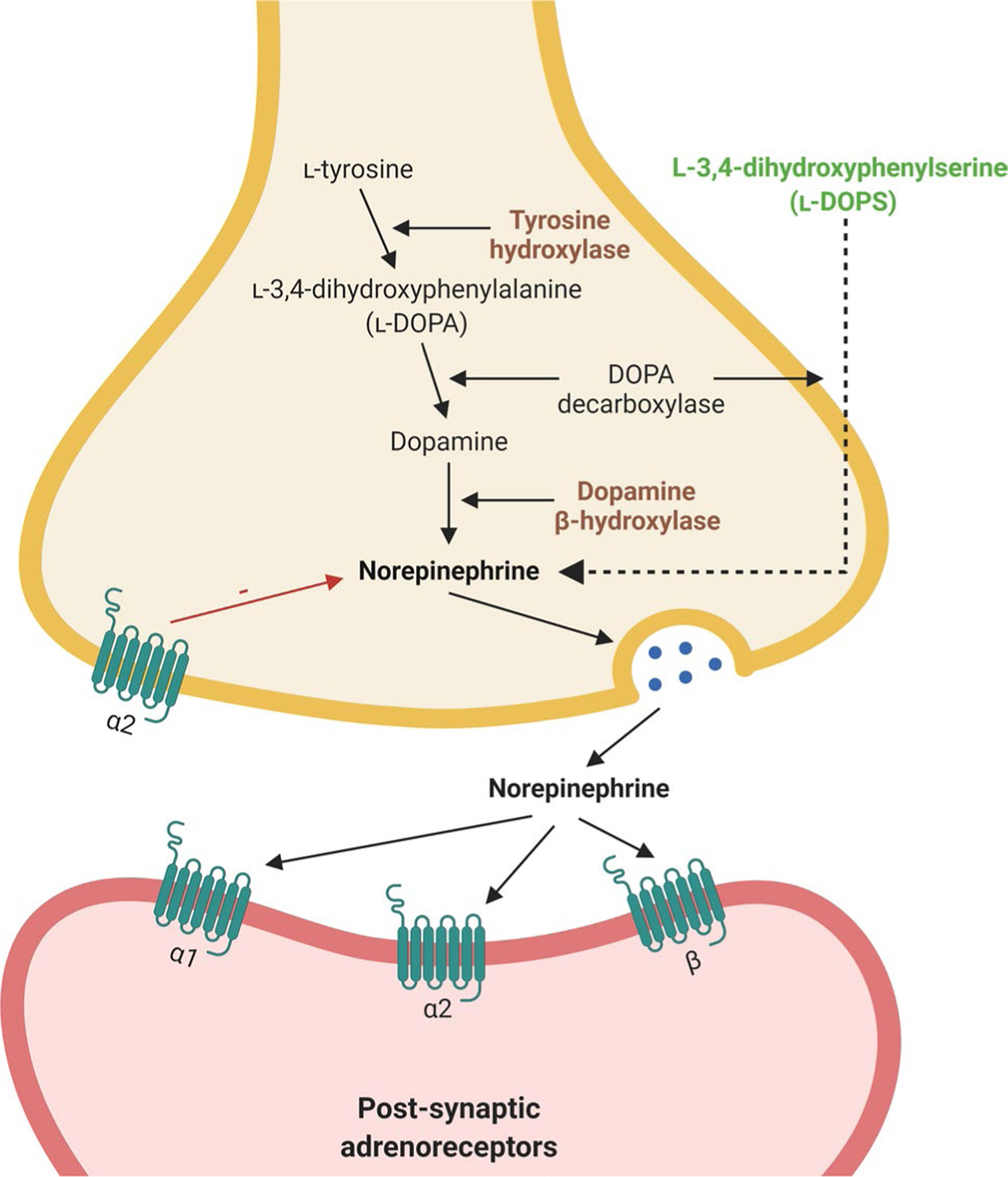
Norepinephrine biosynthetic and signaling pathways in locus coeruleus neurons. l-tyrosine is converted into norepinephrine by a series of enzymatic reactions [70, 113]. Antibody immunoreactivity to key enzymes in the norepinephrine pathway is commonly used as markers of norepinephrine neurons [24]. norepinephrine is released at the synapse, where it binds to G-coupled α- and β-adrenoreceptors to exert its neuromodulatory effects. Agents such as l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine [149] can bypass the pathway and directly increase levels of norepinephrine and, thus, could be used as a potential therapy to compensate for norepinephrine loss following locus coeruleus deinnervation. Created with BioRender.com
