Figure 5. FOXA1 mediates FGFR1 recruitment to chromatin.
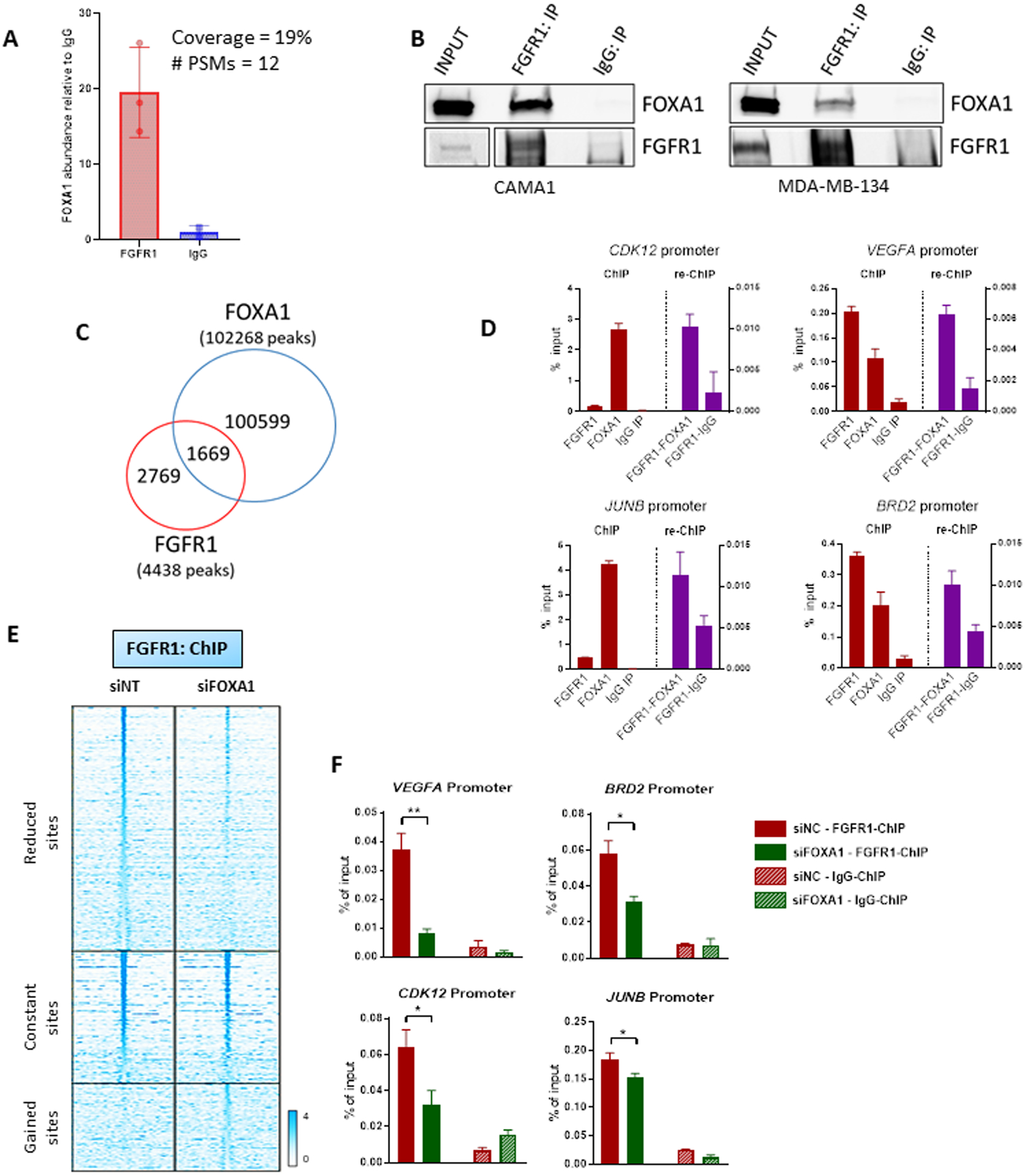
(A) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-FGFR1 followed by mass spectrometry was conducted on mixed nuclear plus chromatin-bound fractions of CAMA13XFLAG-FGFR1 cells. The plot shows the enrichment of FOXA1 in the FLAG-FGFR1-bound fraction compared to IgG control. (B) Co-precipitation of FGFR1 and FOXA1, followed by western blot analysis, in CAMA1 (left panel) and MDA-MB-134 (right panel) cells. (C) Venn diagram of FGFR1 peaks (red circle), identified by ChIP-Seq (in Figure 2A) and FOXA1 DNA binding loci identified by ChIP-Seq (blue circle) in CAMA1 cells. (D) ChIP-reChIP assay performed by sequential ChIP-qPCR with a FGFR1 antibody followed by an antibody against FOXA1 or normal rabbit IgG, at the BRD2, CDK12, VEGFA and JUNB promoters. Enrichment values expressed as percent (%) of input. (E) Heatmaps of ChIP-Seq read densities around the FGFR1 bound regions in CAMA1 cells transfected with Non Targeting (siNT) or FOXA1 siRNAs. Twenty-four h post-transfection, dishes were replenished with IMEM/10% CSS and cells were collected 48 h later for CHIP. (F) ChIP-qPCR confirmation of reduced FGFR1 binding at selected genomic loci, VEGFA (t test, p=0.0071), BRD2 (p=0.0145), CDK12 (p=0.0114), JUNB (p=0.0252) promoters, upon siRNA-mediated FOXA1 knockdown in CAMA1 cells. Enrichment values expressed as percent (%) of input.
