Fig. 5.
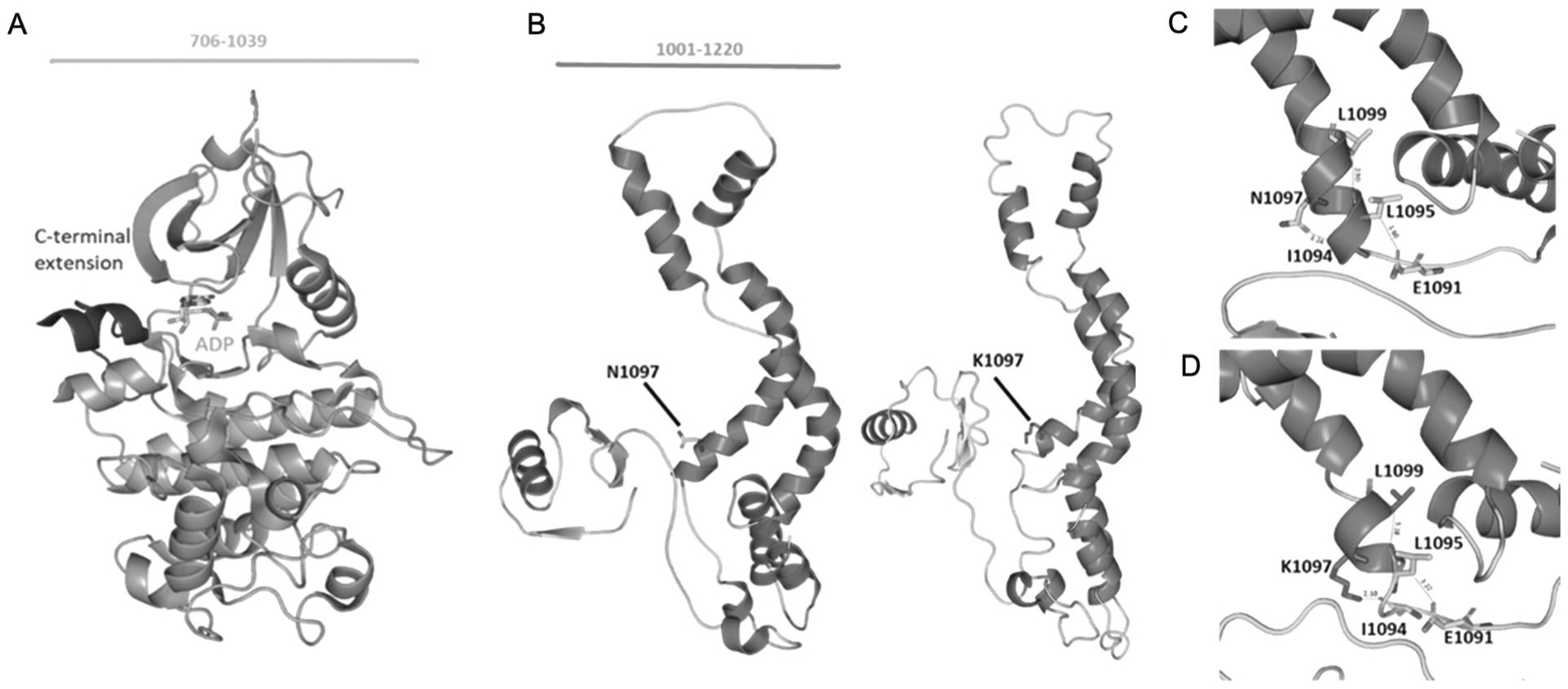
Homology modeling of CDK13. a The crystal structure of kinase domain (PDB ID: 5EFQ). The kinase domain is shown in orange and the C-terminal domain in blue. The number of amino acids visualized is indicated at the top. b Predicted protein models of the wild-type and mutant with asparagine replaced with lysine. The number of amino acids visualized is indicated at the top. c. Asparagine residue at α-helix is predicted to be interacting with residue Ile1094 whereas in the mutant protein. d In the mutant protein, Asparagine is replaced by lysine p.(Asn1097Lys) which modifies the native bond interactions distance. Due to the difference in interaction with nearby residues resulted in shortening of the α-helix
