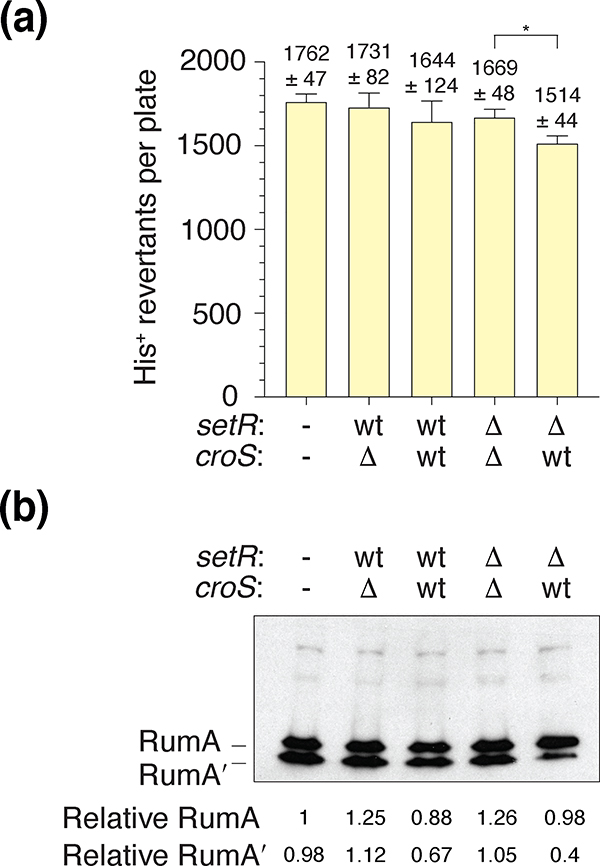
FIGURE 5.
CroSR391 regulation of RumABR391-dependent mutagenesis is dependent on the rumABR391 promoter region.
(a). Spontaneous Histidine reversion mutagenesis assays utilizing MVG114 strains harboring pJM1467 (−/−), a pCC1-derivative carrying the rumABR391 operon under the control of the recA promoter, were transformed with low-copy pGB2-derivatives (pJM1365, pJM1366, pJM1367 and pJM1368) carrying various iterations of the croSR391-setRR391 operon (Table 1). The genotypes of croSR391 or setRR391, either wild-type, or deleted, are indicated. The histogram illustrates the mean colony count for each indicated strain (n = 5). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). An unpaired two-tailed t test was used to compare the mean colony counts for the ΔsetR ΔcroS and ΔsetR croS+ strains. * = p < 0.05. (b). Western blot using an anti-RumA antibody indicating that the level of RumA expressed from the E. coli recA promoter do not change appreciably in the presence, or absence, of SetR or CroS. Numbers reported for the expression levels of RumA and RumA’ are relative to RumA in the left-hand lane.