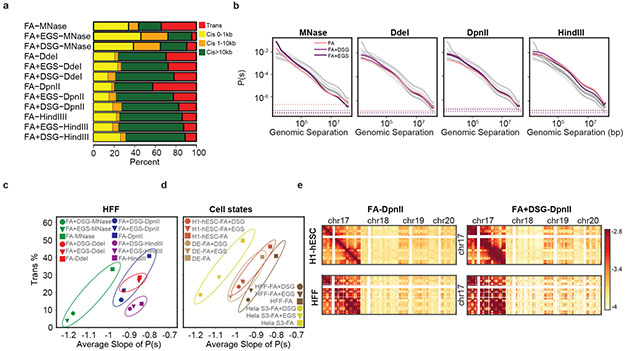
Figure 2: Extra cross-linking yields more intra-chromosomal contacts.
a. Number of valid pairs in each of the 12 HFF protocols by genomic distance.
b. Distance dependent contact probability for 12 HFF protocols. Each plot shows P(s) for experiments performed with indicated nuclease. Color of the lines indicate cross-linkers and gray lines indicate all datasets. Dashed lines show trans level.
c. The percentage of trans interactions versus the average slope of distance dependent contact probability for all cross-linker and enzyme combinations in HFF. Nucleases grouped by colored ovals.
d. Percentage of trans interactions versus average slope of distance dependent contact probability for each cell state. Only experiments cross-linked with FA, FA+DSG or FA+EGS and digested with DpnII are shown.
e. Interactions (log transformed) between chromosome 17 and chromosomes 17, 18, 19 and 20 for FA or FA+DSG cross-linking and DpnII digestion, in H1-hESC and HFF. Total trans interactions for FA-DpnII protocols in H1-hESC: 47.7%, HFF: 42.5% and for FA+DSG-DpnII protocols in H1-hESC: 25% and HFF: 17.3%.