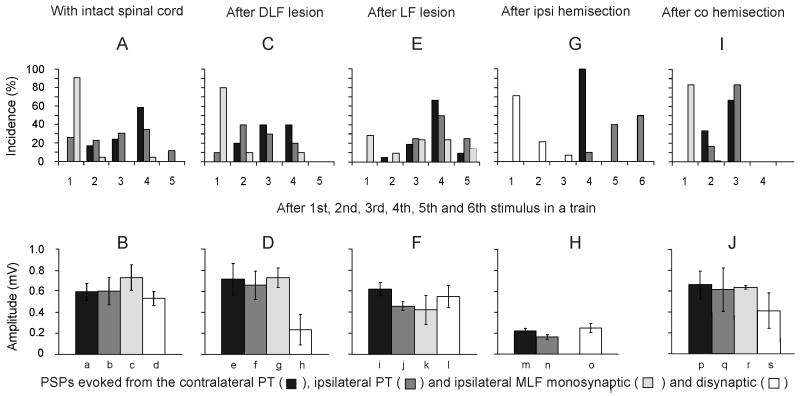
Figure 4. Comparison of stimulus related incidence and amplitudes of short latency EPSPs evoked from the contralateral and ipsilateral PTs and from the MLF.
A, Proportions of motoneurons recorded in preparations with the spinal cord intact in which the first EPSPs were evoked by the 1st - 5th stimuli (100 μA). The plots are for EPSPs with latencies not exceeding 5 ms for the contralateral PT (n = 29) and ipsilateral PT (n = 26), and for monosynaptic EPSPs from the MLF (n = 22). In the remaining motoneurons no EPSPs were induced by such stimuli or no comparison was made of effects of the varying numbers of stimuli. C, E, G and I, as in A but for preparations in which descending tract fibers were transected, as indicated, and for a mixture of monosynaptic and disynaptic rather than only monosynaptic EPSPs from the MLF in G. The lesions were of the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus (DLF; n = 12), the whole lateral funiculus (LF; n = 22), ipsilateral hemisection of the spinal cord (n = 14) and contralateral hemisection (n = 12). B, D, F, H and J, amplitudes of EPSPs evoked in the same samples of motoneurons. Amplitudes of EPSPs with characteristics of disynaptic EPSPs from the PTs were measured for those evoked by the second effective stimuli after having subtracted PSPs evoked by previous stimuli but without including EPSPs preceded by IPSPs evoked by earlier stimuli, or cut short by IPSPs that followed them. Amplitudes of monosynaptic EPSPs from the MLF were measured for those evoked by single stimuli in B, D, F and J but for combined mono- and disynaptically evoked EPSPs in H (bar o) because of difficulties in differentiating between them (see text). Amplitude of disynaptic EPSPs from the MLF were measured only in motoneurons in which no monosynaptically evoked EPSPs were evoked. No statistically significant differences were found between amplitudes of EPSPs evoked from the two PTs in the same preparation (except in F i-j *), or between those from PTs and monosynaptic EPSPs from the MLF in the same preparation. In contrast highly statistically significant differences were found between EPSPs evoked after ipsilateral hemisection and in other preparations (a-m**, b-n*, d-o**).