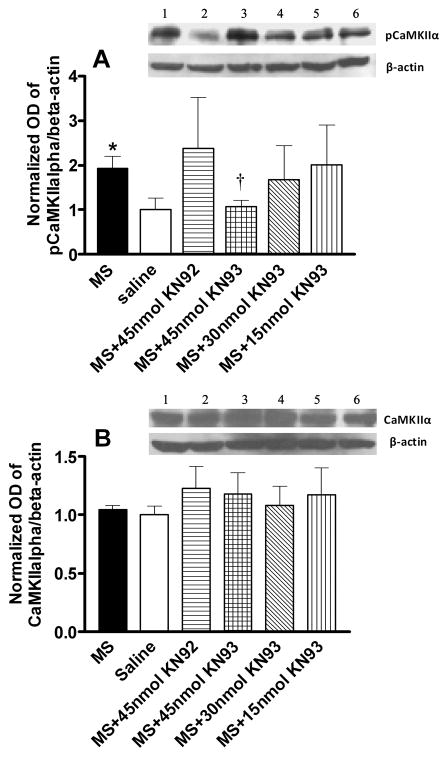
Figure 5. Suppression of morphine-induced CaMKIIα activation by KN93.
Morphine or saline treated mice were administered (i.t.) with KN93 (15–45nmol), KN92 (45nmol), or saline on day 5. One hour later, mice were sacrificed and the lumbar spinal cords were taken for the analysis of CaMKIIα activation using the immunoblotting method, by determining the degree of CaMKIIα autophosphorylation (pCaMKIIα). Morphine enhanced pCaMKIIα expression, without altering CaMKIIα expression. KN93, but not its inactive analog, KN92, reversed morphine enhanced CaMKIIα activation. Data are expressed in Mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, compared with the saline treated group; † p < 0.05, compared with the morphine treated group; n = 4 for each group.