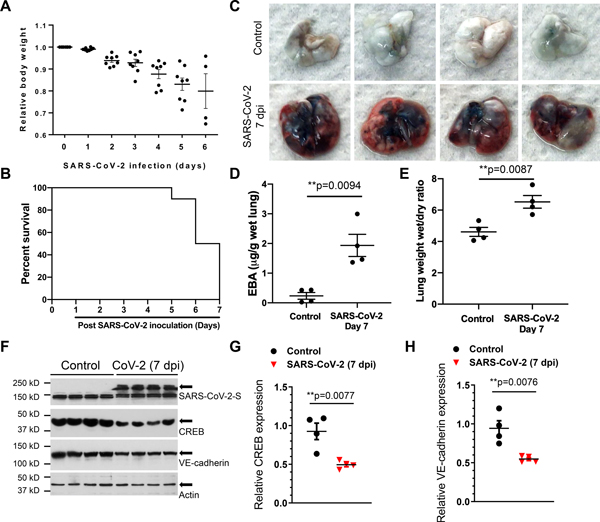
Figure 2. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces lung vascular hyperpermeability and reduces CREB and VE-cadherin expression in K18-ACE-2 mice.
K18-hACE-2 mice (2-month-old) were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (1× 105 p.f.u.) for the indicated days. (A) Mouse body weight was measured post SARS-CoV-2 inoculation. (B) Survival of mice post SARS-CoV-2 infection for the indicated days was monitored and is presented as a Kaplan-Meier plot. (C) Lung vascular leak assessed by Evans Blue Albumin (EBA) dye infusion is shown in representative images from two independent experiments. (D) Quantification of lung vascular permeability (n= 4). Extracted dye contents were quantified by measuring absorption at 620 nm. (E) Lung edema formation by the ratios of the wet lung to dry lung weight was assessed (n= 4). Two-tailed unpaired t test. (F-H) CREB and VE-cadherin were assessed by immunoblotting. Quantification of protein expression was analyzed by ImageJ. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. **P< 0.01, Two-tailed unpaired t test (n=4).