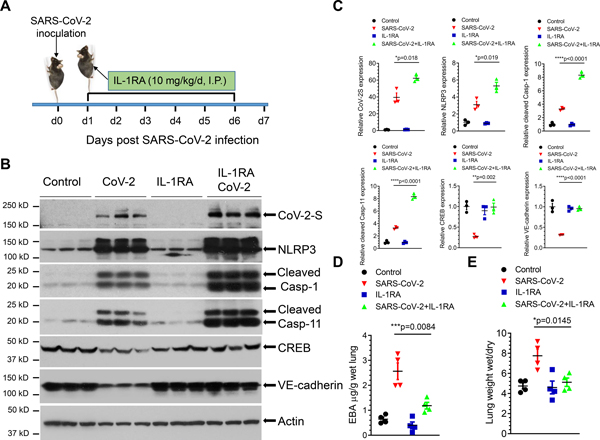
Figure 4. IL-1 receptor blockade by IL-1 receptor antagonist Anakinra prevents SARS-CoV-2-induced lung vascular hyperpermeability and edema.
K18-hACE-2 mice (2-month-old) were infected with a sublethal dose of SARS-CoV-2 (2×104 p.f.u.) for 7 days. (A) Mice were administered IL-1RA Anakinra (10 mg/kg/d) or vehicle by I.P. injection at 24 hours post infection and every day thereafter as shown. (B and C) Lung lysates were assessed for the expression of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, NLRP3, cleaved caspase-1 and caspase-11, CREB, and VE-cadherin by immunoblotting. IL-RA did not prevent the infection-induced expression of the viral spike protein or inflammasome activation but restored the expression of CREB and VE-cadherin. Protein expression levels from blots are quantified in (C). Two-tailed unpaired t test (n=3). *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01 ****P< 0.0001. (D) Lung vascular permeability was determined by lung transvascular albumin flux measurements using Evans Blue Albumin (EBA). (E) Lung edema was determined by ratio of wet-to-dry lung weights (n= 4 in each group). Results are shown as mean ± SEM. *P< 0.05. ***P< 0.001.