Fig. 4.
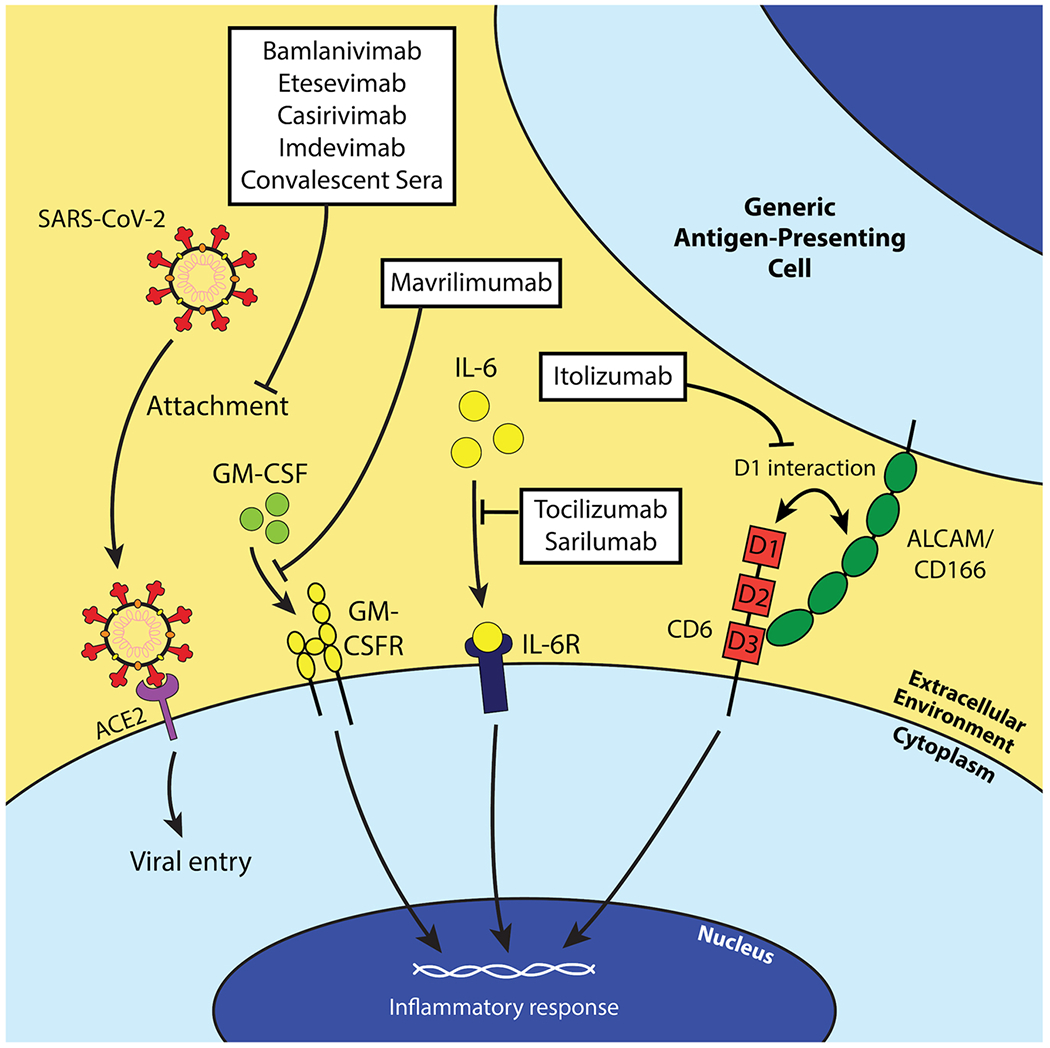
Schematic of the mechanisms of action of each investigated antibody therapy against COVID-19. Most antibody therapies directly target SARS-CoV-2 by neutralizing the virus and preventing entry of the virus into susceptible host cells (bamlanivimab, etesvimab, casirivimab, imdevimab, and convalescent sera). However, mAbs exist against host factors to attenuate inflammatory responses in COVID-19 infection. Mavrilimumab is a GM-CSFR antagonist and prevents GM-CSF’s inflammatory functions (i.e. T cell activation and proliferation, etc.). Tocilizumab and sarilumab are IL-6R antagonists and serve a similar function to mavrilimumab conceptually, and itolizumab binds domain 1 (D1) of CD6 to inhibit its non-adhesive effector functions.
