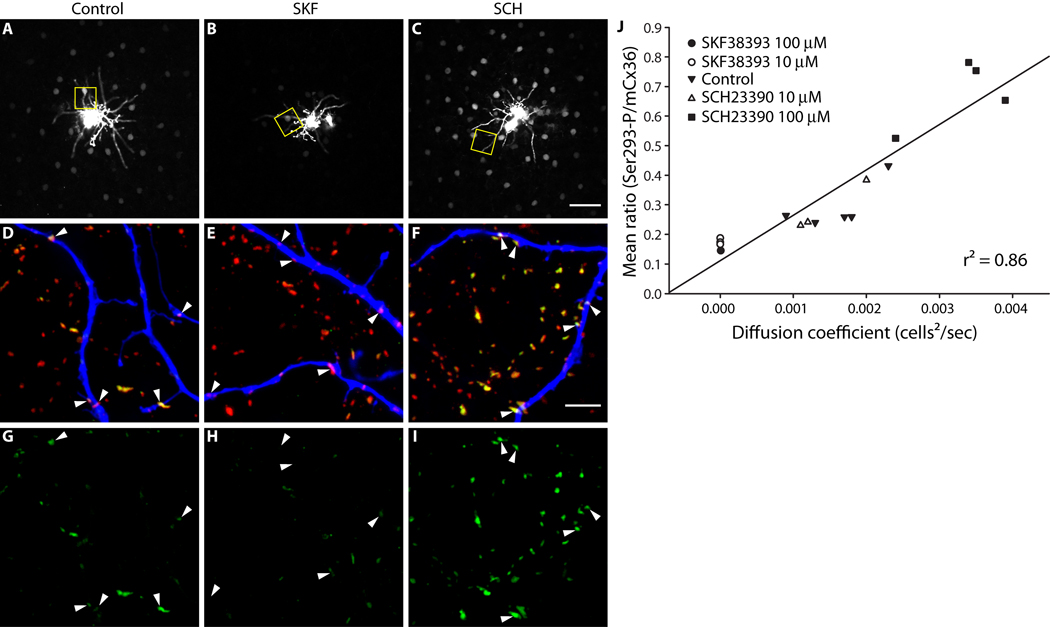
Figure 1. AII amacrine cell coupling is directly related to Cx36 phosphorylation at Ser293.
A–C, Neurobiotin tracer coupling between AII amacrine cells is modulated by dopamine D1R signaling. D1R activation (B, SKF38393, 10 µM) reduced the extent of Neurobiotin diffusion relative to control (A). D1R antagonism (C, SCH23390, 100 µM) increased tracer diffusion. Images are mini-stacks (2 µm in z-depth) focused on the somas of the AII amacrine cells. Yellow boxes highlight areas shown in D–I (at different focal depth). D–F, Cx36 gap junctions, labeled with mCx36 antibody (red) and Ser293-P antibody (green), on and around the dendrites of the injected AII amacrine cell, labeled with fluorophore-conjugated Streptavidin (blue). The Cx36 gap junctions not on the injected cell are primarily on other AII amacrine cells (see Methods). Arrowheads identify prominent Cx36 gap junctions on the injected cells. G–I, Phosphorylation of Cx36 at Ser293, a site known to regulate coupling through Cx36 gap junctions (Ouyang et al., 2005), is also modulated by dopamine D1R signaling. Arrowheads identify the locations of the same Cx36 gap junctions identified in D–F. D1R activation (H, SKF38393, 10 µM) reduced Ser293-P labeling relative to control (G). D1R antagonism (I, SCH23390, 100 µM) increased Ser293-P labeling. J, Quantification of the relationship between AII amacrine cell coupling and Cx36 phosphorylation at Ser293. The mean ratio of Ser293-P intensity to mCx36 intensity (across all Cx36 gap junctions in 3 images per injection) is plotted against the diffusion coefficient for Neurobiotin tracer transfer calculated for each injected AII amacrine cell network. The strong correlation of the data (r2 = 0.86) indicates a direct relationship between AII amacrine cell coupling and Cx36 phosphorylation at Ser293. Images are 2 µm-deep stacks. Scale bar in C is 50 µm; bar in F is 5 µm.