Figure 3.
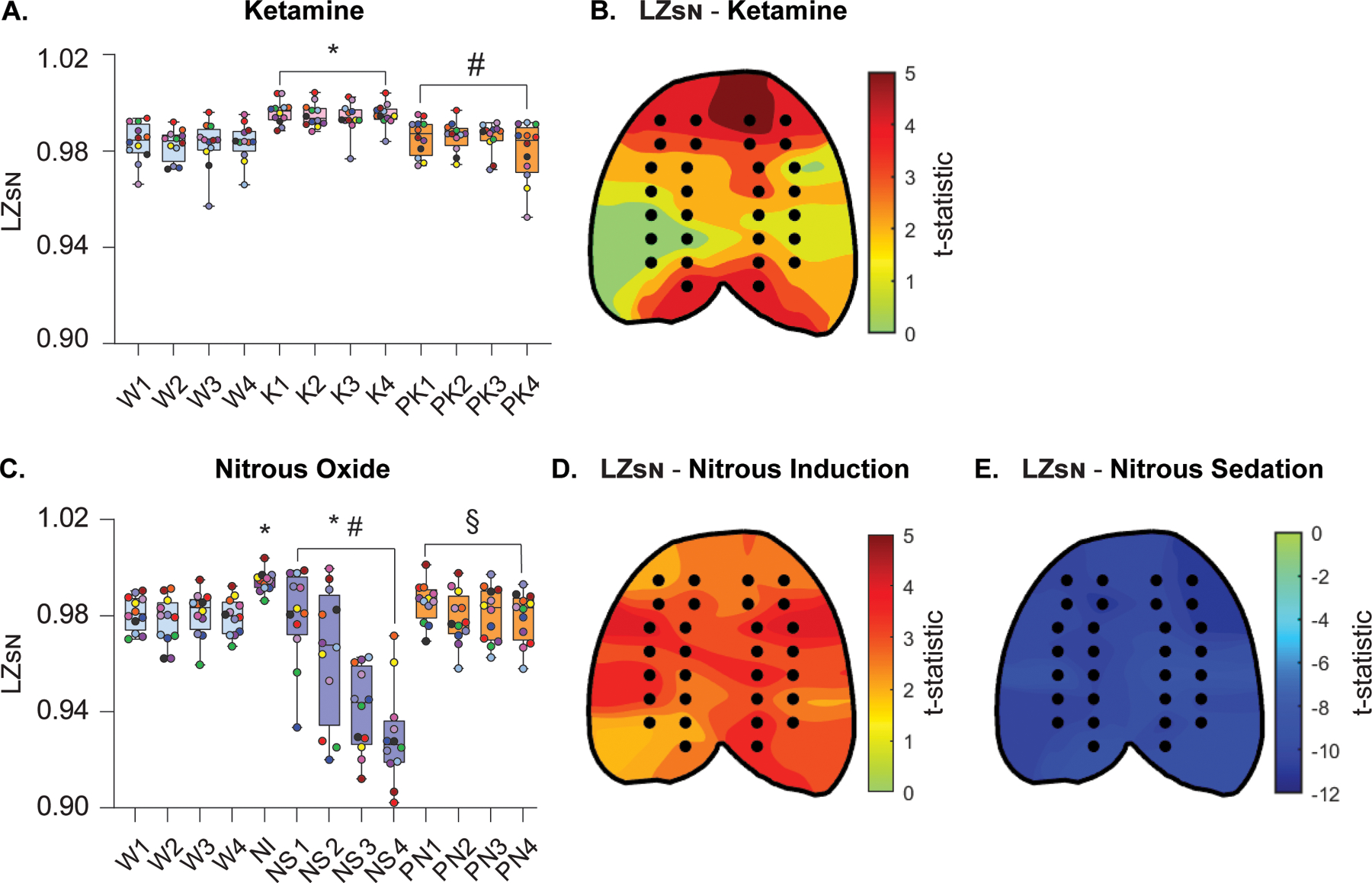
Changes in temporospatial EEG complexity during subanesthetic ketamine infusion and nitrous oxide exposure mirror concomitant changes in cortical acetylcholine levels. Normalized Lempel-Ziv complexity (LZsN) was significantly increased during subanesthetic ketamine infusion, returning to wake levels after the infusion was stopped (A). Changes in LZsN during subanesthetic ketamine infusion were also quantified at the level of single channels (black dots in the topographic plots), demonstrating that the most pronounced changes in temporal complexity, relative to wake, occurred in frontal, posterior parietal, and occipital channel clusters (B). LZsN significantly increased during the first 12.5 min of nitrous oxide exposure (induction phase) as compared to baseline wake state (C). During the subsequent nitrous oxide sedation phase, the LZsN declined to levels significantly lower than that observed during baseline wake. LZsN returned to levels comparable to baseline wakefulness during post-nitrous oxide recovery (C). The most significant increases in temporal complexity during nitrous oxide induction, as compared to baseline wake state, were located in frontotemporal, parietal, and occipital regions (D). Nitrous oxide sedation was characterized by a significant decrease in temporal complexity across the entire cortical surface (E). A linear mixed model with a random intercept for each rat was used for statistical comparisons. Post hoc pairwise tests between states were performed with single-step correction for multiple comparisons via Tukey’s Test. The box plots show the median (horizontal bar) and interquartile range for averaged data over all 12 subjects at each epoch. The whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values within each epoch. The data for each subject are displayed by colored dots, with each color corresponding to a single subject across all epochs. K – subanesthetic ketamine infusion, LZSN - normalized Lempel-Ziv complexity, NI – nitrous oxide induction, NS – nitrous oxide sedation, PK – post-ketamine recovery, PN – post-nitrous oxide, W – wake. *Significant compared to wake, #significant compared to subanesthetic ketamine infusion or nitrous oxide induction, §significant compared to nitrous oxide sedation. The statistical comparisons are shown at P < .05. The exact P values are provided in the text in the results section. The mean, standard deviation, and F-statistics for statistical comparisons are provided in Supplemental Digital Content, Tables 3–4.
