Figure 1. In-frame ESR1-e6 fusions identified in ER+ MBC patients.
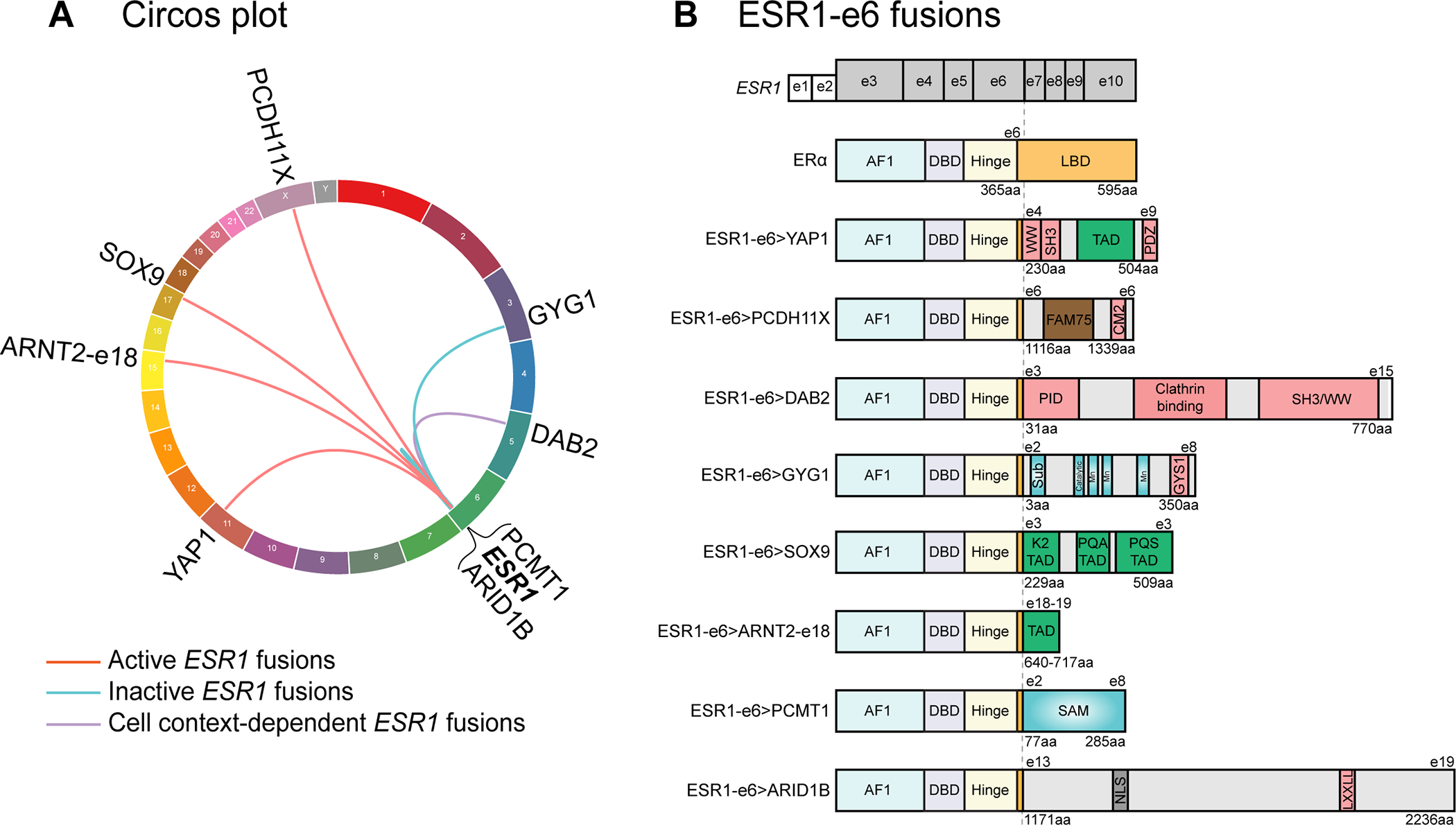
(A) Circos plot depicting ESR1 fusion events identified from ER+ MBC patients. The ESR1 gene is connected to its 3’ partner genes with lines. (B) In-frame ESR1 fusions in ER+ MBC possess a common structure whereby the first 6 exons (two untranslated exons and four coding exons in grey, exons 3–6) of ESR1 fuse in-frame to C-terminal sequences from partner genes. Key for domains in the WT ERα protein: AF1: activation function 1 domain; DBD: DNA-binding domain; Hinge: domain connecting DBD and LBD; and LBD: ligand-binding domain. Pink boxes in partner proteins mediate protein-protein interactions, including WW binding motifs, SH3 binding motifs, a PDZ domain, a conserved motif 2 (CM2), a phospho-tyrosine interaction domain (PID), an interaction with Glycogen Synthase 1 region (GYS1), and a LXXLL motif. Green boxes represent known transcriptional activation domains (TADs). The brown box represents the FAM75 domain of unknown function. Blue domains have enzymatic activities, including substrate binding site (Sub), catalytic site, three manganese binding sites (Mn) and an S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase domain (SAM). The grey box labeled NLS represents a nuclear localization signal.
