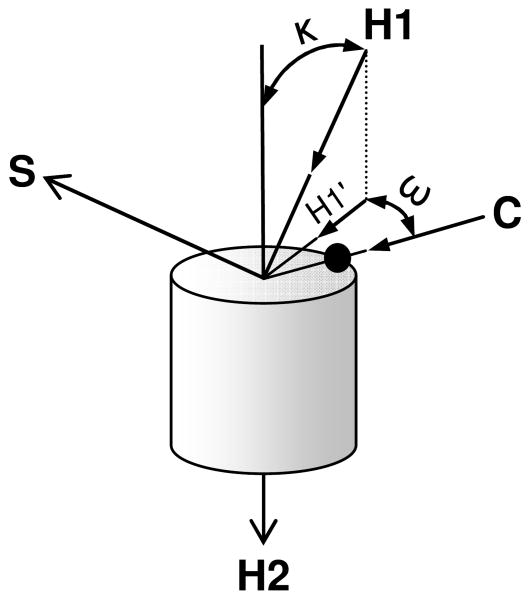
Figure 5.
Definitions of kink (κ) and wobble (ω) angles. H1 and H2 are the helical axes in vector notation before and after a hinge residue. Boldface is a vector. The identities of specific residues used here to calculate H1 and H2 are listed in Figure 6 (36). The axes do not have to intersect in order to calculate κ as the arccos(H1·H2). The ω is defined as follows. A plane normal to vector H2 is created by the vectors S and C, where C is the normalized distance vector between the Cα atom of the hinge residue and vector H2. The dark spot in the figure is the Cα atom of the hinge residue (either L226, V227, or V227L). S is defined as S = H2×C. The vector H1 then is projected into the (S,C)-plane to give vector H1′. The angle between H1′ and C is defined as ω.