Fig. (5).
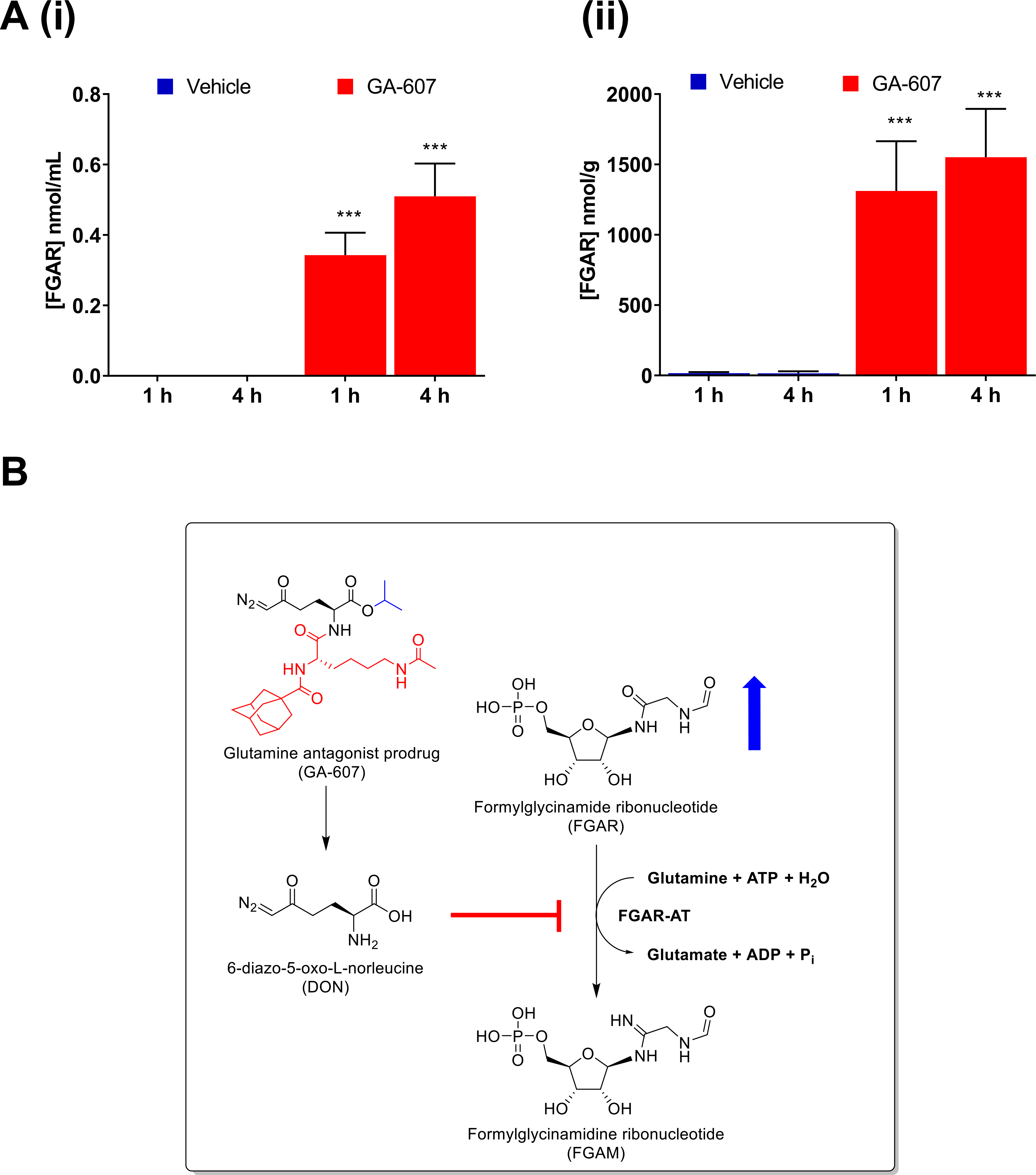
FGAR quantification following GA-607 treatment (3.2 mg/kg SC daily for 4 days) in EL4 tumor-bearing mice. (A) (i) FGAR levels in plasma at 1 and 4 hours after GA-607 or vehicle administration; (ii) FGAR levels in tumor at 1 and 4 hours after GA-607 or vehicle administration. Mean ± S.D. ***p > .001 (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test) (B) Schematic representation of the biochemical pathway regulating FGAR metabolism in tumor tissues and the effect of GA therapy. FGAR-AT, an enzyme in de novo purine synthesis catalyzes the conversion of FGAR, ATP, and glutamine to FGAM, ADP, Pi, ammonia, and glutamate, respectively. Upon cleavage in tumors, GA-607 releases DON. The inhibition of FGAR-AT results in elevated FGAR levels.
