Figure 2.
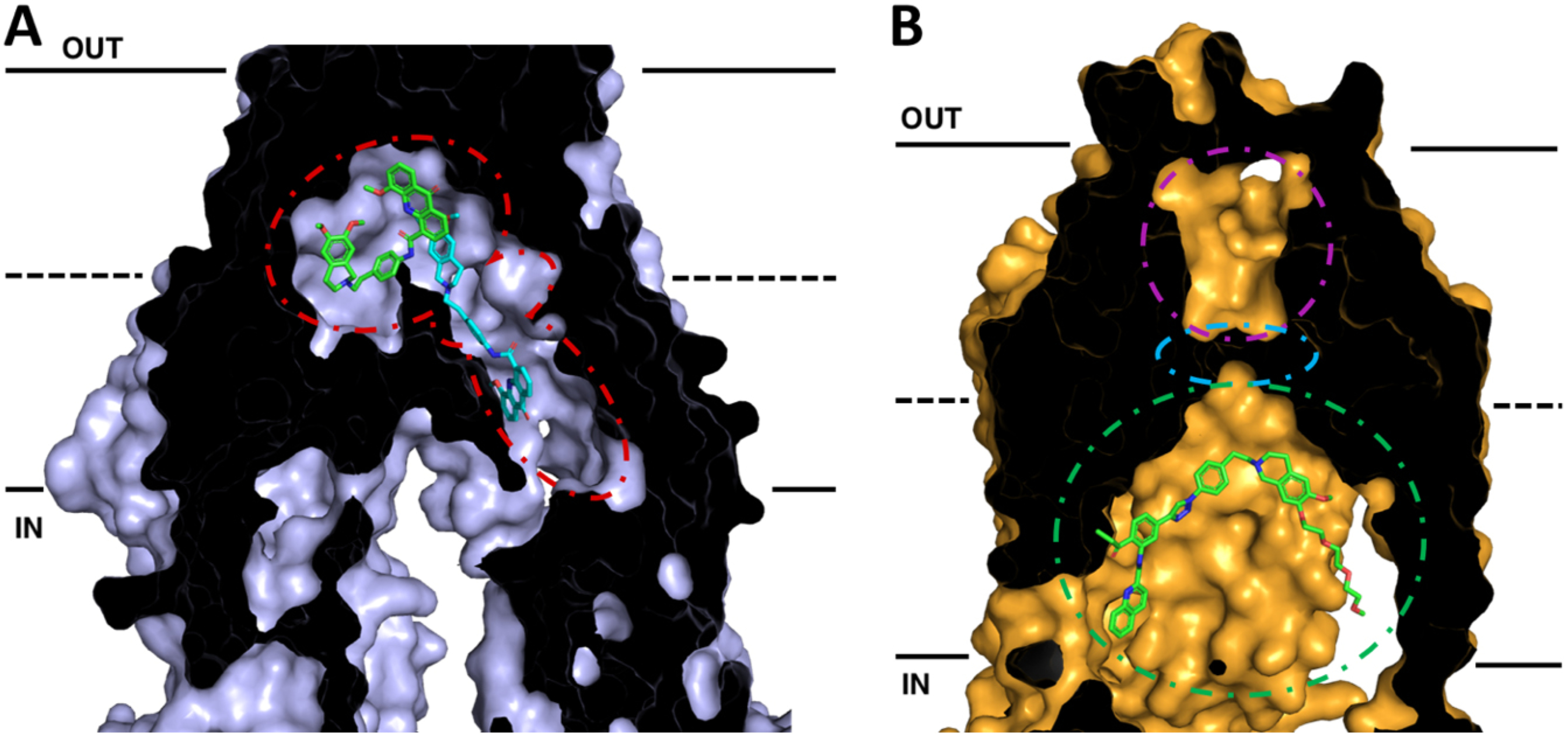
Cross-sections of cryo-EM structures of P-gp and ABCG2 with bound inhibitors in inward-facing conformations. The membrane is delineated by solid black lines. The extracellular space (OUT) is at the top of the image, and the intracellular space (IN) is at the bottom. (A) Cryo-EM structure of P-gp bound with two molecules of the inhibitor elacridar. One molecule (green) is bound to the drug-binding pocket while the other (cyan) passes through a smaller binding region, the vestibule, before extending into an access tunnel. (B) Cryo-EM structure of ABCG2 with bound the tariquidar analog MB136. MB136 is bound to the top of cavity 1 (green) under the leucine gate (cyan) and is believed to stop conformational changes that would allow the substrate to pass into cavity 2 (magenta) and be effluxed. Adapted from PDB: 7A6C (P-gp)[96] and 6FEQ (ABCG2)[112]
