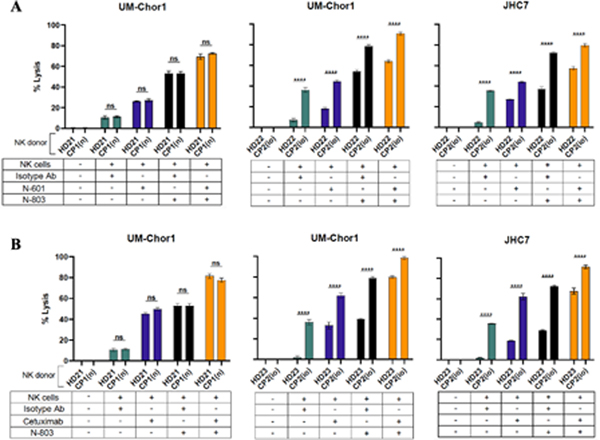
Fig. 5. Chordoma patients’ NK cells mediate significant lysis of chordoma cells and are enhanced with N-601 (anti-PD-L1), cetuximab (anti-EGFR), and N-803 (IL-15 superagonist).
Two chordoma cell lines (UM-Chor1, JHC7) were used as targets for healthy donor NK cells or chordoma patient NK cells in 111In-release killing assays. Combination treatment assays were performed by co-incubating chordoma cells with N-601 (A), cetuximab (B), or isotype control antibody (A and B) where indicated. Healthy donor NK cells (A and B), treatment-naïve chordoma patient (CP1(n)) NK cells (A and B), or previously-treated chordoma patient (CP2(io)) NK cells (A and B) were treated with N-803 where indicated and used as effectors. All E:T ratios are 20:1. Statistical analyses were done by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. Results shown are the means ± SEM of technical triplicate measurements and are representative of two independent experiments with recurrent chordoma patients and one experiment with a treatment-naïve chordoma patient.