Figure 2.
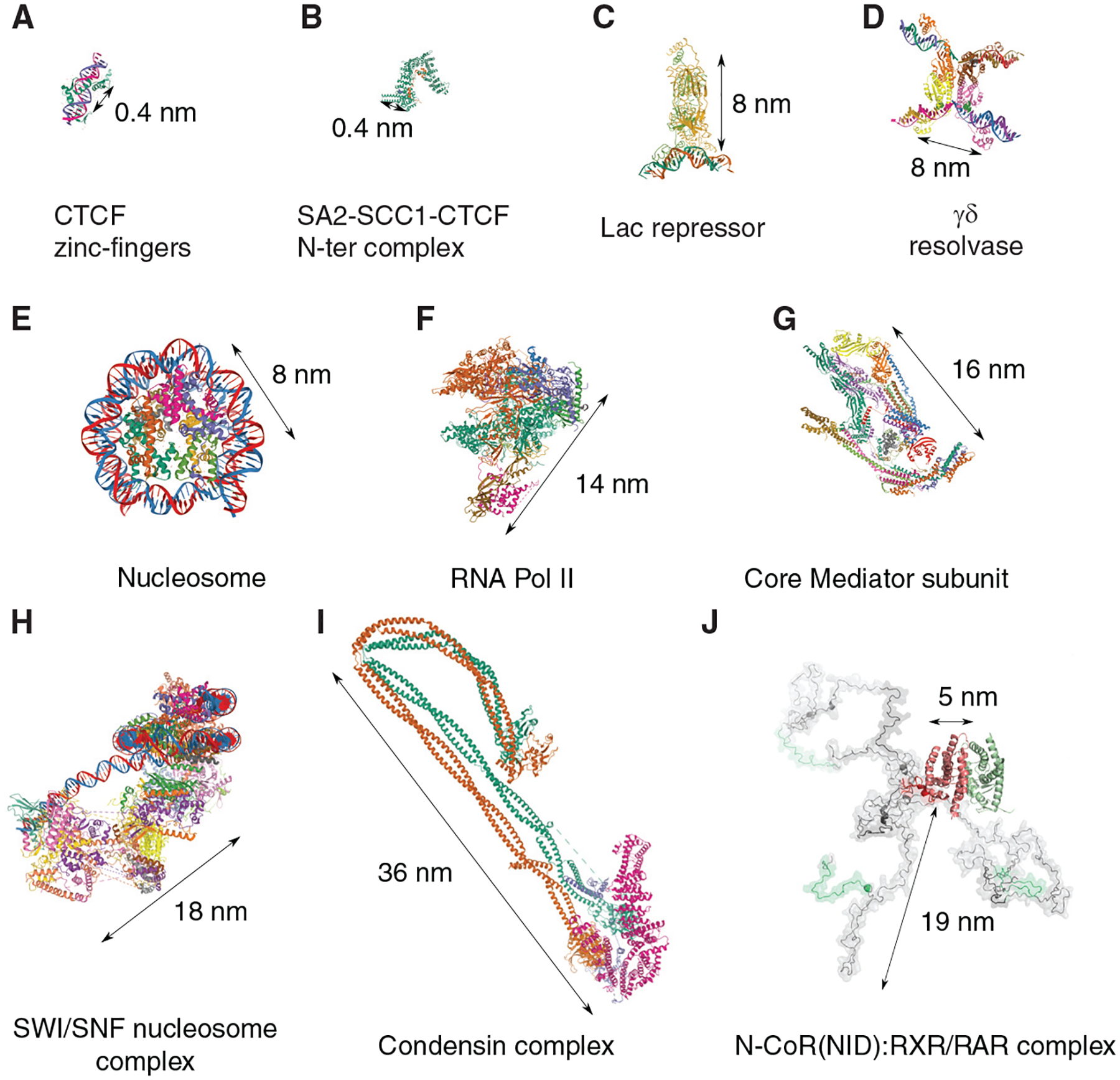
Atomic-resolution structures and physical sizes of factors involved in chromosome organization and function. (A) CTCF zinc-fingers 4–8 bound to DNA (5YEG) (Yin et al. 2017), (B) SA2-SCC1 subunit of cohesin (green) bound to CTCF amino-terminal fragment (orange) (6QNX) (Li et al. 2020b), (C) Lac repressor bound to DNA (1LBG) (Lewis et al. 1996), (D) γδ resolvase in complex with site I DNA (1ZR4) (Li et al. 2005), (E) human nucleosome complex (3AFA) (Tachiwana et al. 2010), (F) complete 12-subunit RNA Pol II (5FJ8) (Armache et al. 2005), (G) crystal structure of the 15-subunit core Mediator complex from Schizosaccharomyces pombe (5N9J) (Nozawa et al. 2017), (H) SWI/SNF in complex with nucleosome (6TDA) (Wagner et al. 2020), (I) condensin complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (6YVU) (Lee et al. 2020), and (J) folded domains and three putative models of the asymmetric forms of the N-CoRNID:RXR/RAR complex are displayed (Cordeiro et al. 2019).
