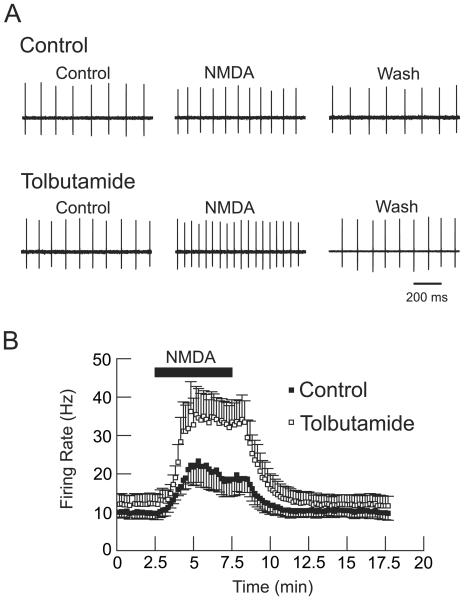
Figure 9. Loose-patch recordings of STN neurons showing tolbutamide (100 μM)-induced augmentation of the acceleration in firing rate produced by NMDA (20 μM).
A, Single-cell action potentials recorded extracellularly from an STN neuron in the presence of NMDA with and without tolbutamide. Note that the excitatory effect of NMDA is more pronounced in the presence of tolbutamide. B, Averaged responses from 8 STN neurons. Note the significant increase in NMDA-dependent firing rate produced by tolbutamide superfusion (P < 0.001, paired t-test; n = 8). Tolbutamide-alone produced a small increase in firing rate but this was not statistically significant (P = 0.0599).