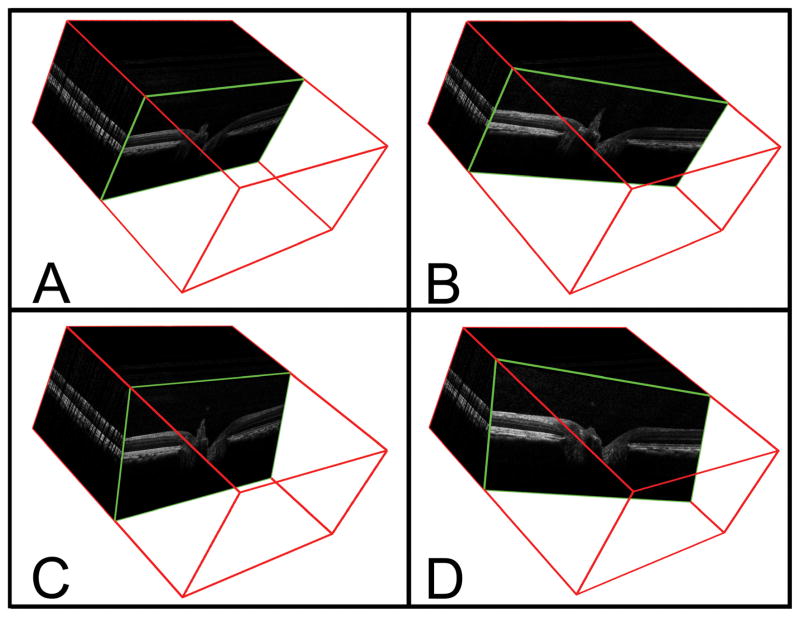
Figure 3. Method of identifying interpolated B-scans from the SD-OCT volumetric reconstruction.
A – A representative acquired B-scan is shown within the 3D volume (enclosed within a red cube) generated from a 290 × 768 horizontal raster scan. The angle of rotation of the B-scan is 90° and the angle of incidence is 0°.
B – The interpolated B-scan shown has been generated following a 20° clockwise rotation (angle of rotation = 70°); the angle of incidence is unchanged,
C – The interpolated B-scan shown has been generated following a −20° change in the angle of incidence.
D – The interpolated B-scan shown has been generated using an angle of rotation of 70° and an angle of incidence of −20°.