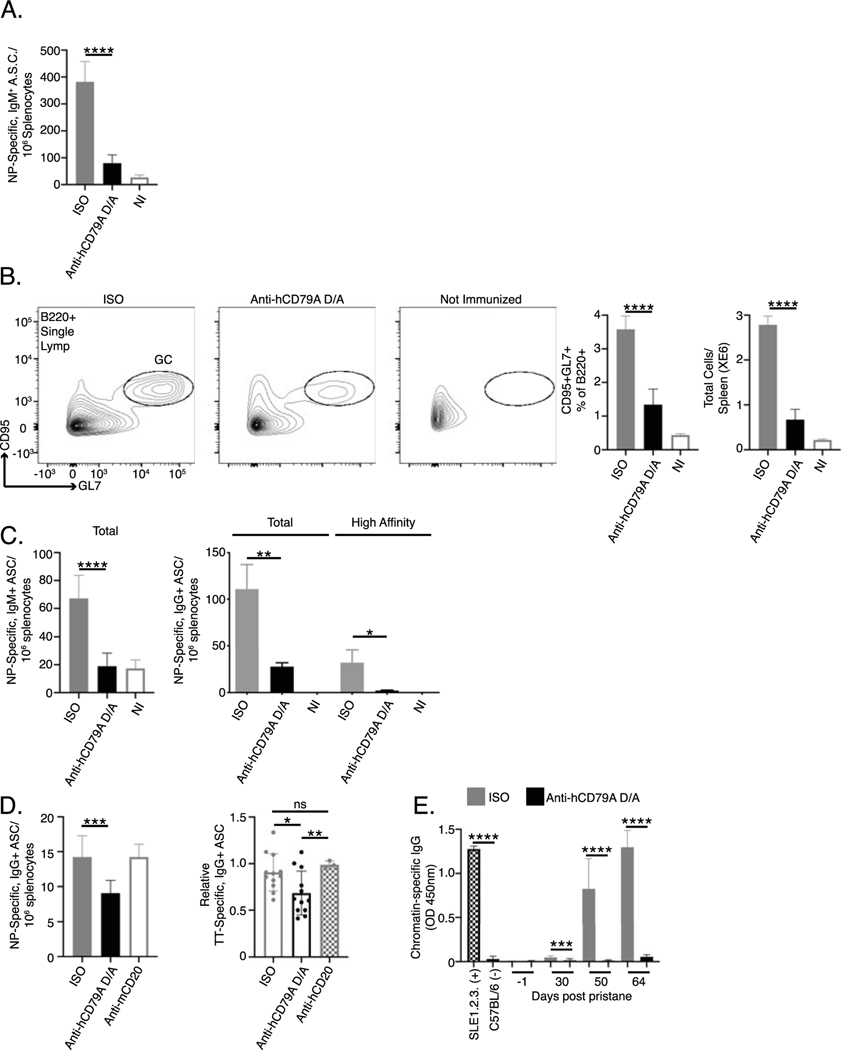
Fig 5. Anti-human CD79A treatment inhibits B cell immune responses.
(A.) ELISPOT analysis of NP-specific, IgM+ ASC 7 days after immunization with NP59-ficoll. 24 hours prior to immunization, cCD79A mice received 250 μg IP injections of either anti-human CD79A D265A or control hIgG4. (B.) Flow cytometric analysis of germinal center B cell induction 5 days after immunization with 0.1% SRBC in PBS. 24 hours prior to immunization, cCD79A animals received 250 μg IP injections of either anti-human CD79A D265A or control hIgG4. On day 5 post immunization, RBC-lysed splenocytes were stained with antibodies recognizing B220, CD95, and GL7. (C.) ELISPOT analysis of NP-specific IgM+ (left) and IgG+ (right) ASCs 16 days post immunization with NP-Ova in alum. 24 hours prior to immunization cCD79A mice received 250 μg IP injections of either anti-human CD79A D265A or control hIgG4. For detection of total IgM and IgG anti-NP ASC, plates are coated with NP19-BSA. For detection of high affinity IgG anti-NP ASC, plates are coated with NP2-BSA. (D.) ELISPOT analysis of NP- (left) and tetanus toxoid-specific (right) IgG+ ASC following overnight incubation with anti-human CD79A D265A. NP-specific ASC were generated by immunizing cCD79A knock-in mice with NP-Ova in alum and harvesting spleens 16 days later. 10E6 RBC-lysed splenocytes were put into 1 mL cultures containing 25 μg of either anti-human CD79A D265A, anti-mouse CD20, control hIgG4, or control mIgG2a. After 18-hour incubations, cells were washed and loaded onto ELISPOT plates coated with NP19-BSA. n= 3 wells per condition. This experiment was repeated 3 times. PBMCs were isolated from peripheral blood obtained from subjects receiving Tdap booster vaccines 7–10 days prior. 5E6 PBMCs were put into 1 mL cultures containing 25 μg of either anti-human CD79A D265A, anti-human CD20, or control hIgG4. After overnight incubation, cells were washed and loaded onto tetanus toxoid coated ELISPOT plates. n= 3 subjects who’s PBMCs were incubated with anti-human CD79, n= 1 subject who’s PBMCs were also incubated with anti-human CD20. Points represent individual counted wells. (E.) Effects of serial, weekly treatments with hIgG4 D265A anti-hCD79A in pristane-induced development of autoantibodies (Anti-chromatin IgG ELISAs). Pooled sera from aged/diseased SLE1.2.3 mice and wild-type C57BL/6 served as positive and negative controls, respectively. n = 20 male and 20 female cCD79A mice per treatment arm. Error bars show SEM. Student’s t-test used to evaluate statistical significance. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001. All data represents at least 3 independent experiments, representative data shown.