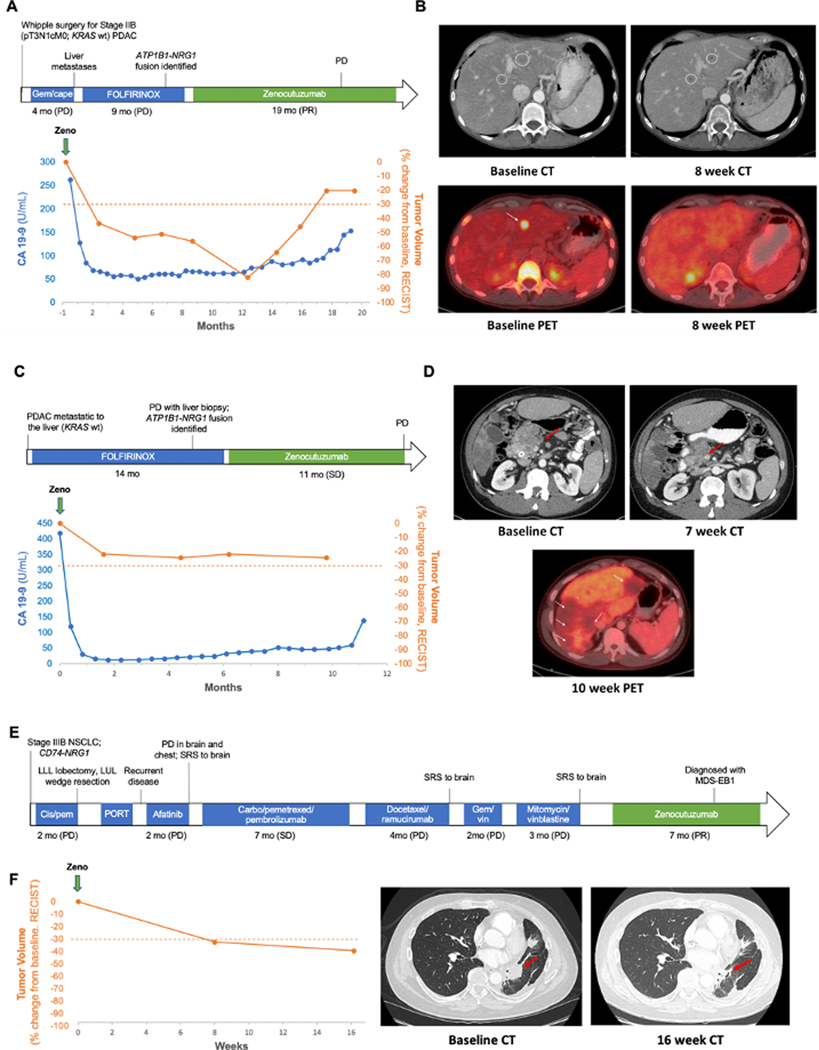
Figure 4. Clinical responses to Zeno.
A. Clinical course of a 50-year-old man with ATP1B1-NRG1 fusion-positive PDAC treated with Zeno (top) including tumor volume and CA 19–9 levels during Zeno treatment (bottom). Best overall response is indicated for each therapy, including progressive clinical disease (PD) and partial response (PR) as defined by RECIST v1.1. B. Representative tumor imaging of this patient’s liver metastases at baseline and eight weeks into treatment with Zeno. C. Clinical course of a 34-year-old man with ATP1B1-NRG1 fusion-positive PDAC treated with Zeno (top) including tumor volume and CA 19–9 levels during Zeno treatment (bottom). Best overall response is indicated for Zeno [stable disease (SD) as defined by RECIST v1.1]. D. Representative tumor imaging from this patient showing a CT scan of the pancreas performed at baseline and seven weeks into treatment with Zeno, and a PET scan 10 weeks into treatment showing non-FDG avid liver metastases (no baseline available). E. Clinical course of a 52-year-old man with CD74-NRG1 fusion-positive NSCLC treated with Zeno after six prior lines of systemic therapy and multiple courses of radiation. Best overall response is labeled for each therapy, including clinical PD/SD, and PR as defined by RECIST v1.1. F. Tumor shrinkage in this patient depicted graphically (left) and by representative tumor imaging (right) performed at baseline and 16 weeks into Zeno treatment. Abbreviations: cape, capecitabine; carbo, carboplatin; gem, gemcitabine; MDS-EB1, myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts-1; pem, pemetrexed; PORT, post-operative radiation therapy; vin, vinorelbine.