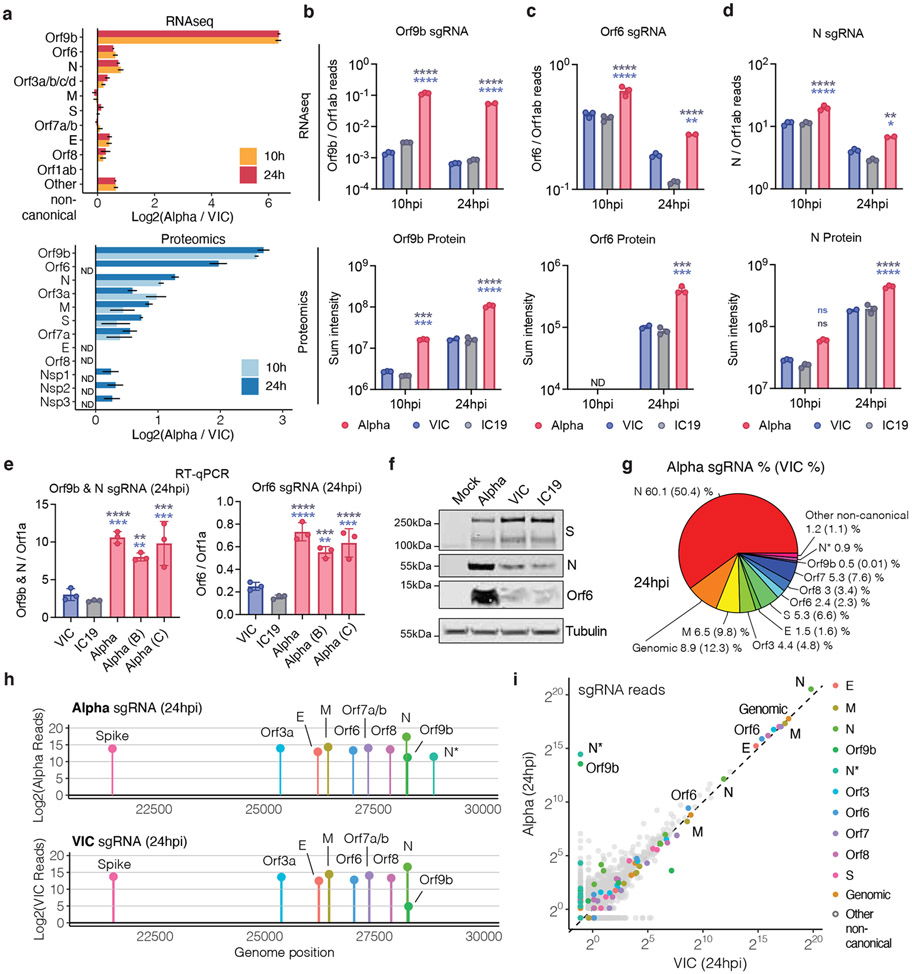
Figure 3. SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant upregulates innate immune antagonists at the subgenomic RNA and protein level.
a. Log2 ratio of Alpha to VIC sgRNA normalised to total genomic RNA per time point and virus (top). Log2 ratio of summed peptide intensities per viral protein comparing Alpha to VIC (bottom) (n=3) b. c. and d. Quantification of Orf9b (b), Orf6 (c) and N (d) sgRNA from RNAseq dataset (top) and summed peptides per viral protein (bottom). e. Quantification of Orf9b & N (left) or Orf6 (right) sgRNA abundance via RT-qPCR. f. Representative western blot of Orf6, N and S expression in infected Calu-3 (2000E copies/cell) at 24 hpi (n=3). g. Pie chart depicting proportion of total sgRNA mapping to each viral sgRNA for Alpha. VIC percentages in parentheses. h. sgRNA log2 normalised counts (dot height) projected onto their identified start sites on the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Canonical and two non-canonical sgRNAs (Orf9b and N*) are depicted. i. Scatter plot of sgRNA abundance in Alpha or VIC at 24 hpi. Grey dots indicate other non-canonical sgRNAs containing a leader sequence but no clear start codon. Mean +/− SEM (a-e). Two Way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-test (c-e). * (p<0.05), ** (p<0.01), *** (p<0.001), **** (p<0.0001). ns: non-significant. ND, not detected.