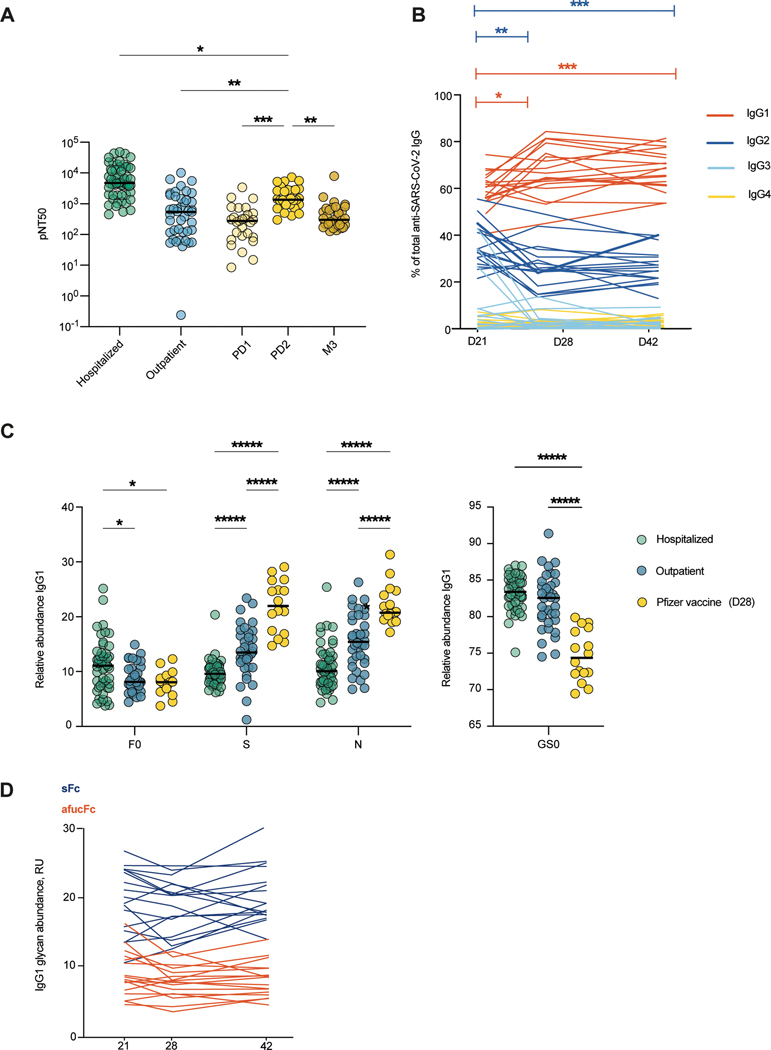
Figure 3. mRNA vaccination elicits high neutralizing antibody titers with Fc glycoforms distinct from infection-induced IgG phenotypes.
(A) The half-maximal SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralizing titers (pNT50) in healthy adults following mRNA vaccination (yellow n=29) or in COVID-19 outpatients on study day 28 (blue n=42) are shown. PD1: post-dose 1, PD2: post-dose 2, M3: month 3. (B) Longitudinal analysis of IgG subclasses is shown for day 21, 28, or 42 post-primary vaccination (n=17). (C) SARS-CoV2 IgG1 Fc posttranslational modifications were analyzed in samples from patients hospitalized with COVID-19 (n=52), COVID-19 outpatients (day 28 n=36) and in participants who received the Pfizer BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (day 28 post primary vaccination, n=16). F0: afucosylation, S: sialylation, N: bisection, GS0: galactosylation. (D) Longitudinal analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG1 Fc afucosylation (afucFc, red line) and sialylation (sFc, blue line) is shown on day 21, 28 or 42 post-primary vaccination. The median values in (A and C) are depicted with a black line. P values in (A) were calculated using Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn’s correction, in (B) using mixed effect analysis with Geisser-Greenhouse and Tukey’s corrections, and in (C) using a twoway ANOVA and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.