Figure 6.
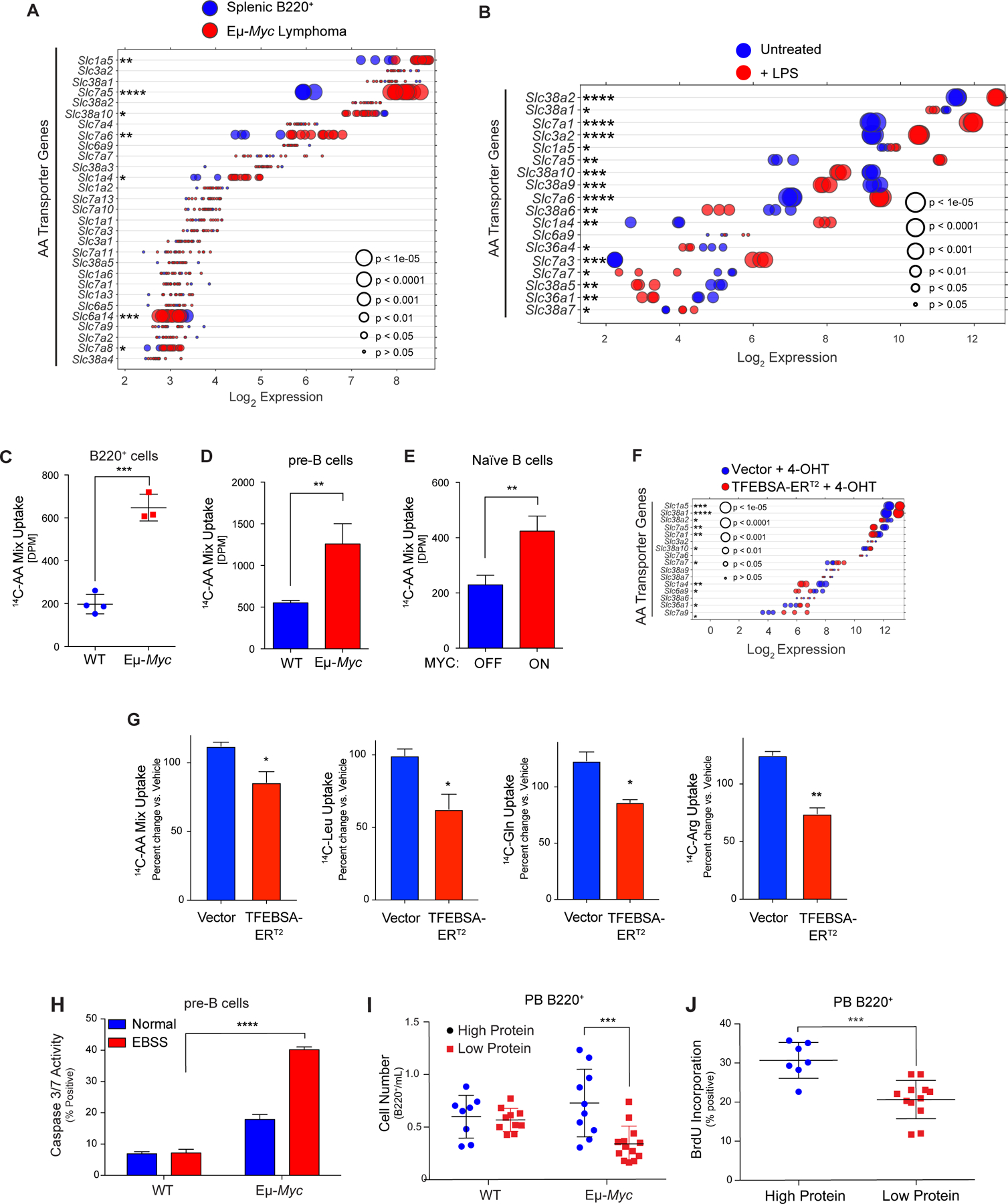
MYC induces expression and activity of select amino acid transporters in B lymphoma. A and B, Gene expression of amino acid transporters in (A) of splenic WT and neoplastic Eμ-Myc B cells (GSE32239), and (B) untreated and LPS-stimulated mouse splenic B cells (GSE37222). Log2 mRNA levels are shown in a dot plot that is ordered based on expression; each dot represents one sample, and the size corresponds to its statistical significance as shown. C-E, Uptake of 14C-labeled amino acids in (C) WT vs. Eμ-Myc B220+ BM cells; (D) WT vs. Eμ-Myc pre-B cells cultured in IL-7; and (E) untreated (MYC-Off) or LPS-stimulated (4 hr, MYC-ON) primary splenic B cells. F, Log2 gene expression profile of genes encoding select amino acid transporters are shown in a dot plot ordered based on their expression in Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells expressing vector or TFEBSA-ERT2 4 days after treatment with vehicle or 4-OHT; each dot represents one sample, and its size corresponds to its statistical significance as shown. G, Uptake of indicated 14C-labeled amino acids in Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells expressing vector or TFEBSA-ERT2 after treatment with vehicle or 4-OHT (4 days). H, Pre-B cells isolated from WT vs. Eμ-Myc mice were plated in normal or EBSS media for 3 hr and apoptosis measured via Caspase3/7 activity. I, WT and Eμ-Myc littermate mice were switched to a chow containing either high (20%) or low (6%) protein three weeks after birth. The number of peripheral blood (PB) B220+ cells were determined after 1 week. J, 6-week-old WT and Eμ-Myc littermate mice were switched to a chow containing either high (20%) or low (6%) protein for one week and were then injected i.v. with BrdU and incorporation was measured in PB B220+ cells. Statistical analysis: C-E and G-J, Students t-tests were performed.*, p ≤0.05; ** p ≤0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001; ****, p ≤ 0.0001.
