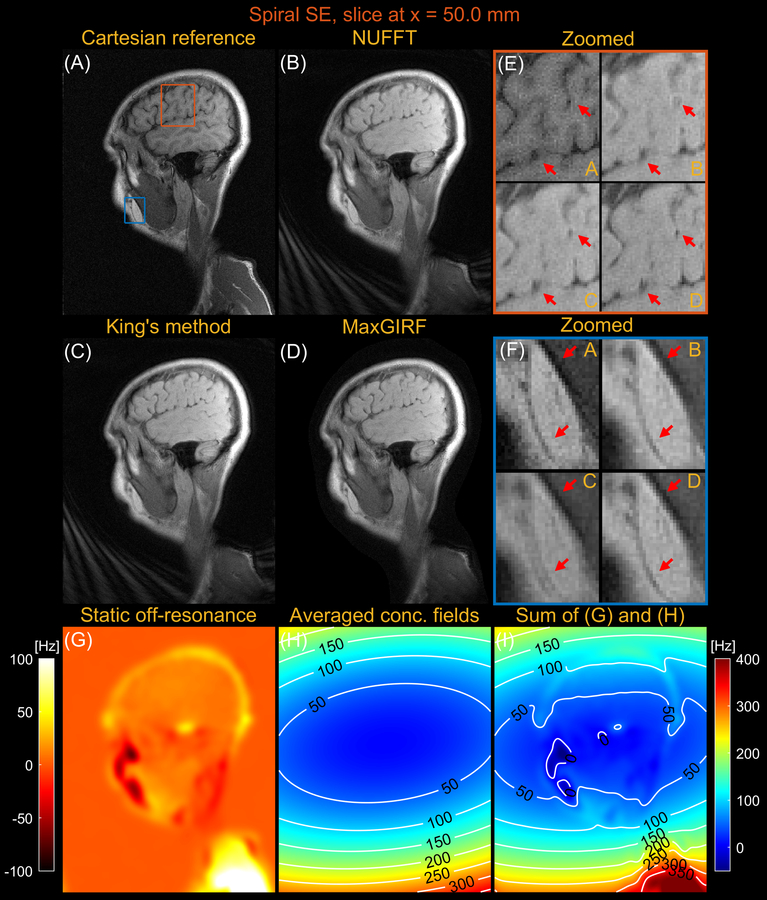
Figure 8.
Sagittal spiral spin-echo imaging of a healthy volunteer at 0.55T off-isocenter (x = 50.0 mm). Comparison of image reconstructions using (A) comparator Cartesian spin-echo image, (B) NUFFT reconstruction, (C) King’s method without static off-resonance correction, and (D) MaxGIRF reconstruction with static off-resonance correction (Low-rank approximation L = 30). (E) Zoomed-in image of a brain region (orange box). (F) Zoomed-in image (blue box). (G) Static off-resonance map. (H) Time-averaged concomitant fields map. (I) Sum of the static off-resonance map and time-averaged concomitant fields map. King’s method may adversely increase blurring artifacts (e.g., blue box) compared to NUFFT reconstruction when the static off-resonance in a region counteracts the concomitant fields. However, MaxGIRF with static off-resonance correction correctly handles such regions as shown in (F) and provides “sharper” delineation of brain tissue boundaries in (E) compared to King’s method.