Figure 1. Schematics of the assays developed to assess antibody recognition of SARS-CoV-2 on the surface of infected and transfected cells.
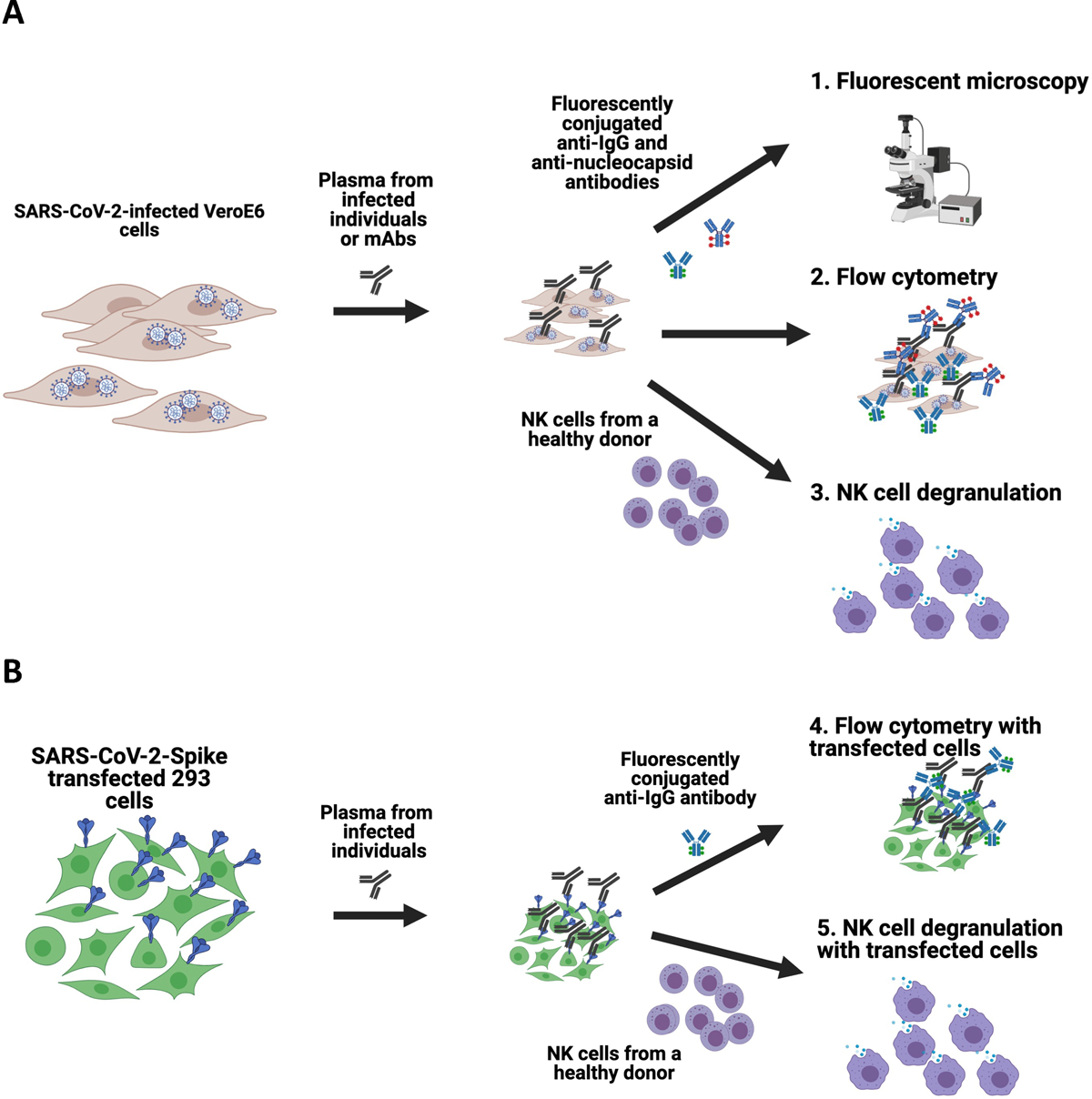
Vero E6 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 and then incubated with plasma from infected individuals or anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike-specific monoclonal antibodies. Cells were then either stained with fluorescently conjugated anti-IgG and anti-Nucleocapsid antibodies to assess using fluorescent microscopy or flow cytometry, or incubated with NK cells from a healthy human donor to measure the capacity of antibodies to mediate NK cell degranulation (A). For transfected cell assays, 293 cells were transfected with SARS-CoV-2 Spike plasmid, incubated with plasma from infected individuals and then stained with fluorescently conjugated anti-IgG to assess using fluorescent microscopy or flow cytometry, or incubated with NK cells from a healthy human donor to measure the capacity of antibodies to mediate NK cell degranulation (B).
