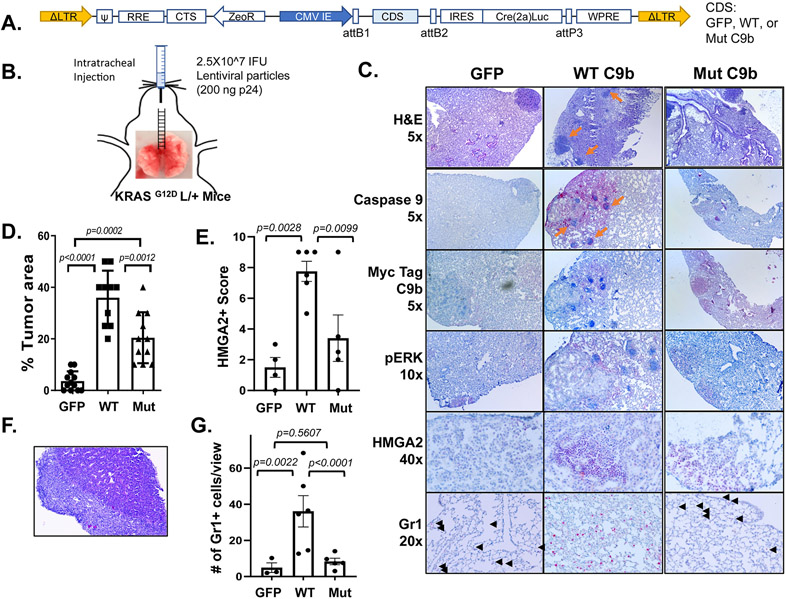
Figure 6. C9b cooperates with KRAS activation driving lung tumorigenesis.
KRASG12D L/+ mice with intratracheal injection (B) of lentiviral particles containing GFP-, WT-, or Mut C9b-Cre(T2a)Luc (A) developed lung tumors (C) at 32 wks post injection. Immunohistochemical staining (C) with indicated antibodies shows the expression of Myc-tagged WT or mutant C9b, ERK activation (pERK), and HMGA2 in tumors and the presence of Gr1+ cells in the lung (black arrowheads). Orange arrows point to the clusters of immune cells observed. The percent replacement of normal lung parenchyma by tumor cells based on H&E and pERK signal (n=12 for GFP, 10 for WT C9b, and 11 for Mut C9b, D), the HMGA2 positivity score (E), and the number of Gr1+ cells per view (20X magnification, G) (n=4 for GFP, 6 for WT C9b and Mut C9b, average of 3 views per mouse for E&G) in each group are shown. F. Metastasis observed in the liver (H&E, 10x magnification) in a mouse with WT C9b expression. Data in D,E,G are means ± SEM combined from 2 independent intratracheal injection experiments. Adjusted p values are determined by ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparison test.