FIGURE 2 |.
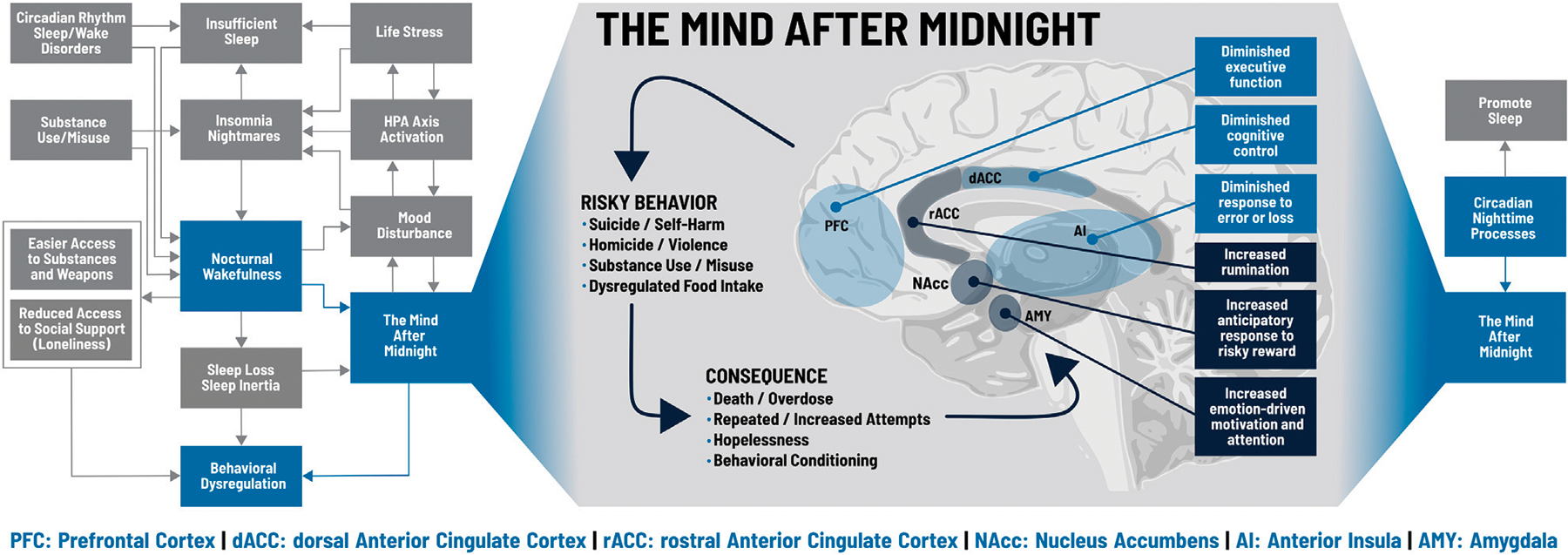
The Mind after Midnight. Blue boxes on the left and right sides indicate key processes within the model discussed in the text; grey boxes indicate additional components not specifically addressed. During nocturnal wakefulness, upregulation of the amygdala (AMY), nucleus accumbens (NAcc), and the rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) increase emotionally driven salience, attention, and motivation, skew anticipation of risky rewards, and drive excess rumination. Conversely, impairments in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and anterior insula (AI) lead to executive dysfunction, diminished cognitive control, and insensitivity to error or loss. These changes promote a cycle of risky behaviors and consequences that can spiral out of control. Figure adapted from Perlis et al. (2016b).
