Figure 5: Fgf8 reductions condense the malleus and middle ear.
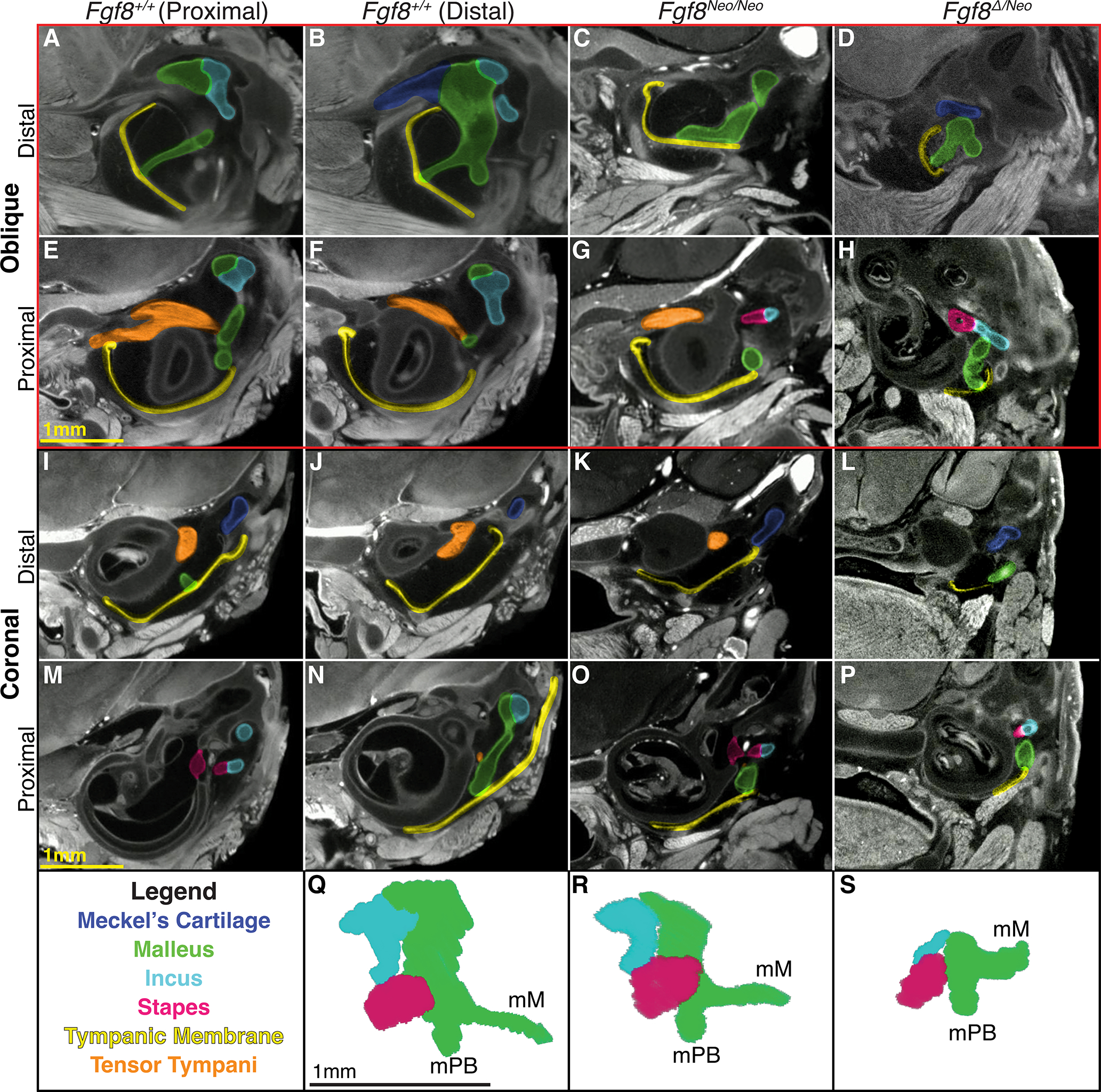
Micro-CT scans of the middle ear of Fgf8+/+ (WT; 2 left columns), Fgf8Neo/Neo (3rd column) and Fgf8Δ/Neo (4th right column) neonatal skulls. WT sections in the first column are proximal to WT sections in column 2. Rows 1 and 2 (red rectangle) are oblique sections through the malleus and rows 3 and 4 are coronal sections through similar regions. Distal sections are shown in rows 1 and 3; more proximal sections of each sample are shown in rows 2 and 4. A, B) In WT, the manubrium of the malleus (green) is shown where it contacts the tympanic membrane (TM; yellow) creating a V shape at the point of contact. C,D) In, Fgf8Neo/Neo and Fgf8Δ/Neo the manubrium is dorsally rotated away from the TM, which is small and dysmorphic. E,F) In WT, the tensor tympani muscle (orange) curves around the sphenoid-temporal articulation. The tensor tympani muscle is reduced in G) Fgf8Neo/Neo, and possibly absent in H) Fgf8Δ/Neo (see also K,L). I,J) In WT, the tympanic cavity is large separating the middle ear and cochlea, but in K) Fgf8Neo/Neo the cavity is reduced in size and becomes smaller in L) Fgf8Δ/Neo. M,N) The incus (light blue) articulates with the stapes (pink) at the oval window of the otic capsule proximal to the malleus (panel N is distal to M). O,P) In the mutants, the middle ear is compressed, such that all 3 middle ear bones lie in one plane, with the incus and stapes rostral to the malleus. The stapes appears morphologically normal in all dosage levels. (Q-S) Three-dimensional reconstructions of the middle ear of Q) Fgf8+/+ (WT), R) Fgf8Neo/Neo, and S) Fgf8Δ/Neo; malleus, incus and stapes. Manubrium of Malleus (mM),process brevis of the malleus (mPB). Scale bar in E applies to A-H, scale bar in M applies to I-P, and scale bar in Q applies to Q-S.
