Fig. 3.
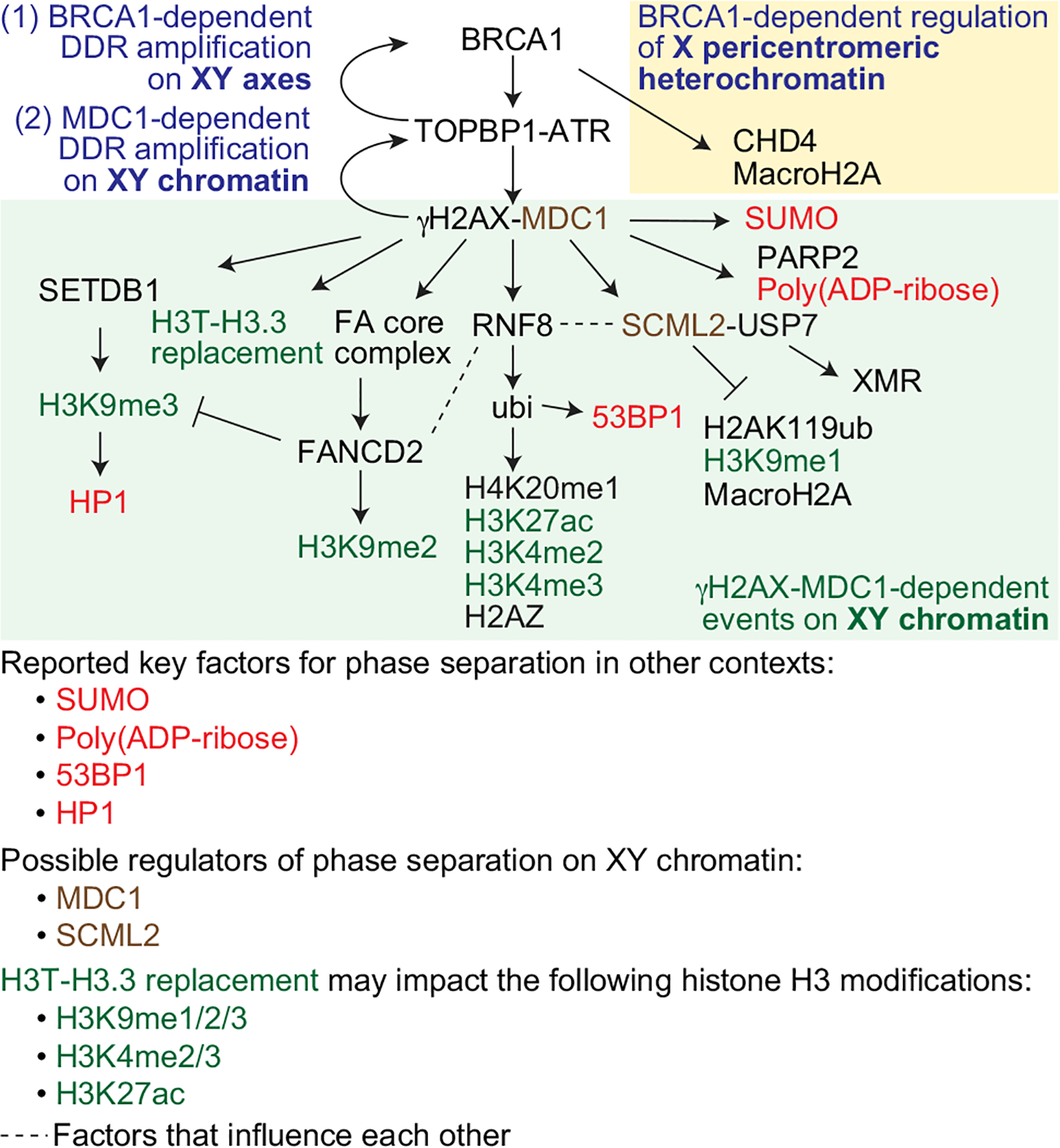
Model for molecular mechanisms in MSCI, including roles for DDR factors, other chromatin-associated proteins, and histone modifications. MSCI is initiated by BRCA1-dependent DDR amplification on the XY axes (1). BRCA1 has an additional function in the establishment of X pericentromeric heterochromatin (yellow box). MDC1-dependent DDR amplification subsequently takes place on XY chromatin (2; green box). Here, we focus on DDR signaling events, recruitment of chromatin factors such as HP1, and histone modifications that occur on XY chromatin. Since the formation of the XY body may involve phase separation, it should be noted that SUMO, Poly(ADP-ribose), 53BP1, and HP1 (shown in red), all of which are related to MSCI, and which are regulated downstream of MDC1, are reported to be key factors for phase separation in other contexts. MDC1 and SCML2 (shown in brown) are possible regulators of phase separation on XY chromatin, as discussed in this review. H3T-H3.3 replacement may impact the following histone H3 modifications: H3K9me1/2/3, H3K4me2/3, and H3K27ac (shown in green). Dashed lines signify factors that influence each other. A key of color codes for various factors is shown at the bottom
