Figure 7. Expression of MUC1 in SCLC tumor tissues.
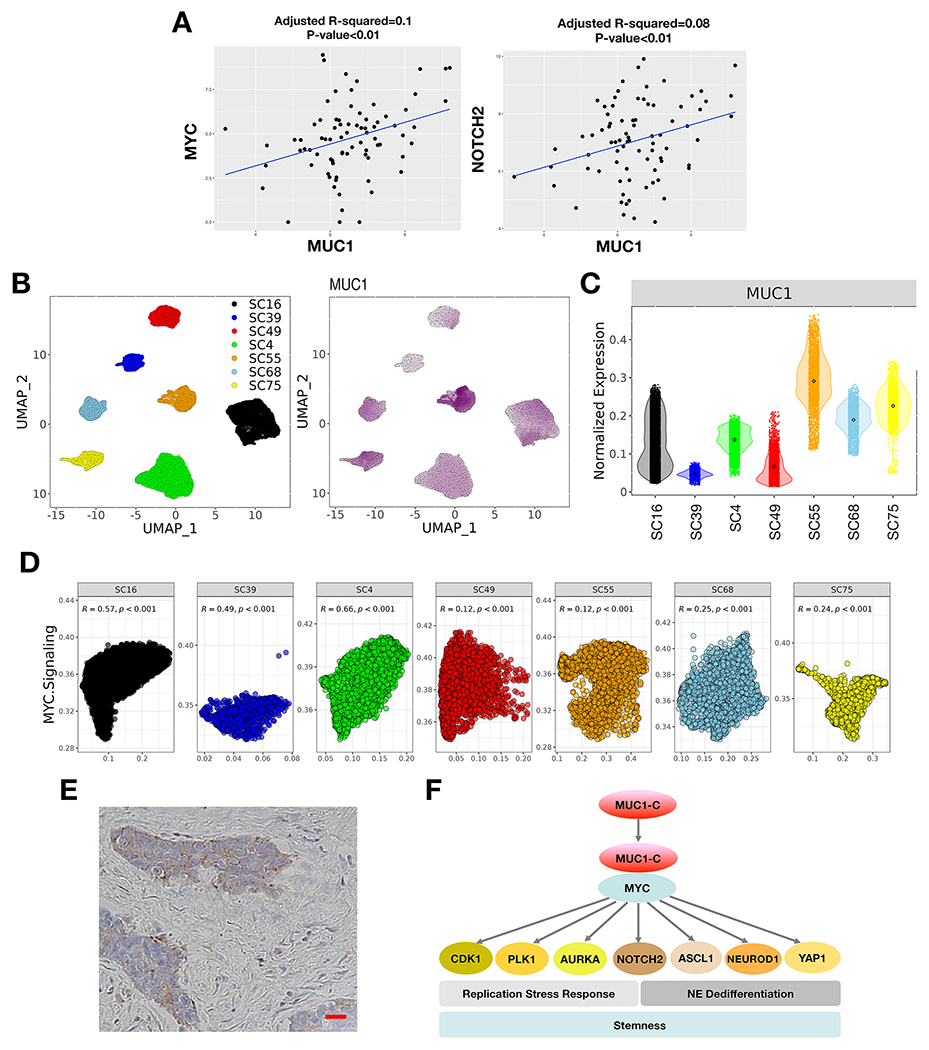
A. Analysis of the GSE60052 SCLC bulk RNA-seq dataset demonstrating significant correlations of MUC1 with MYC and NOTCH2 expression in SCLC tumor tissues. B. Analysis of the GSE138267 SCLC scRNA-seq dataset demonstrating MUC1 expression in clusters of SCLC cells obtained from 7 patient-derived CDX models. C. Distribution of MUC1 expression in the 7 CDX models. D. Significant associations of MUC1 expression with activation of the HALLMARK MYC TARGETS V1 pathway in individual tumors. E. Representative IHC staining of MUC1-C expression in SCLC tumor tissue. Bar represents 50 microns. F. Proposed model for MUC1-C in driving SCLC progression. MUC1-C activates MYC and E2F target genes that contribute to the RSR and mitotic progression. MUC1-C→MYC signaling also drives expression of NOTCH2 and NE dedifferentiation. MUC1-C thereby integrates activation of the dysregulated MYC and E2F pathways and RSR with NE dedifferentiation, stemness and self-renewal in SCLC cells.
