Fig. 4. Resptress score identifies distinct molecular subtypes among various cancer types.
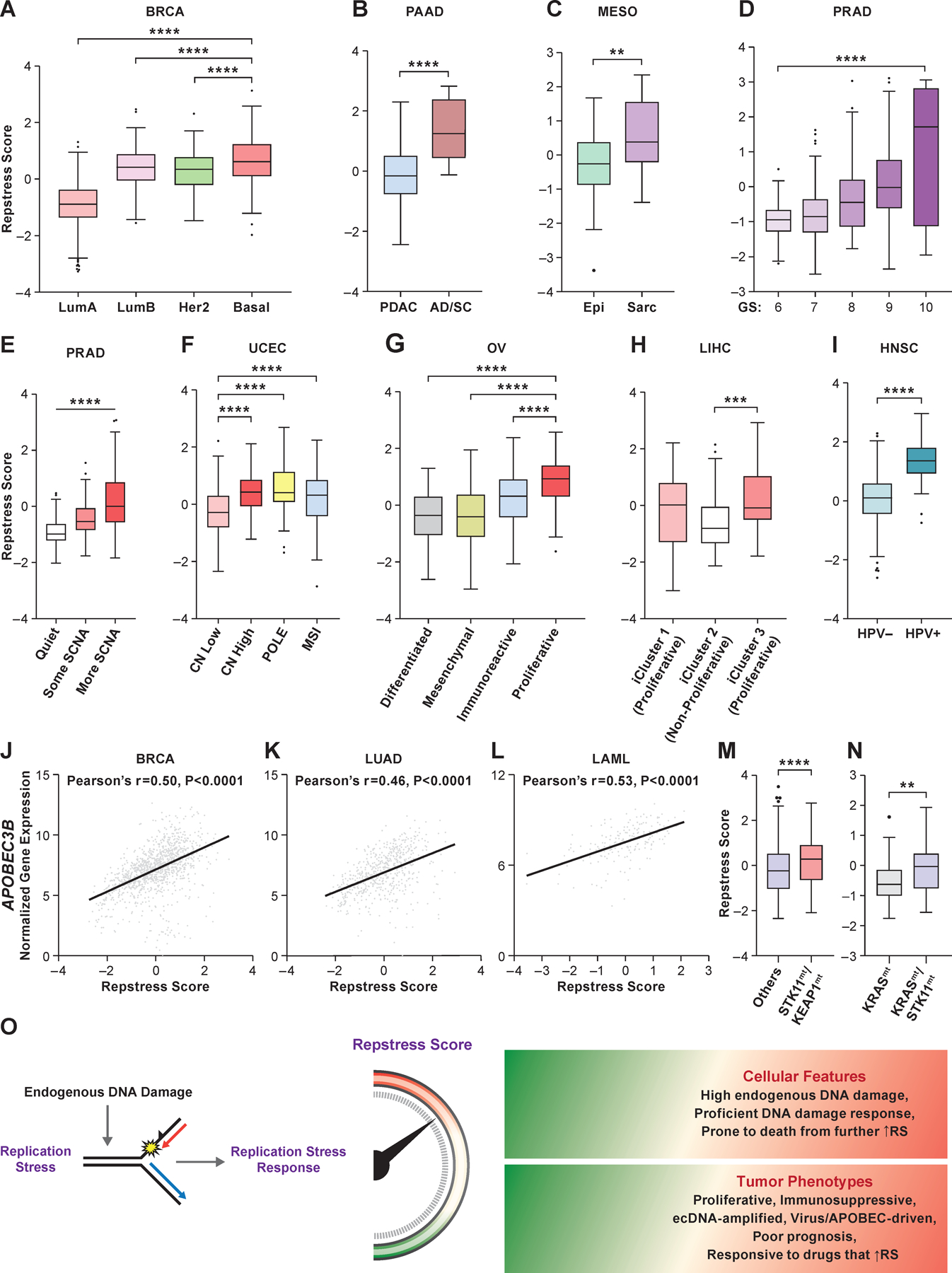
(A), Repstress scores among different breast cancer molecular subtypes
****: P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(B), Repstress scores in pancreatic cancers with adenocarcinoma (PDAC) vs. adenosquamous (AD/SC) histology
****: P < 0.0001 by Mann-Whitney U test
(C), Repstress scores in malignant mesothelioma with epithelioid (Epi) vs. sarcomatoid or mixed epithelioid and sarcomatoid (Sarc) histology
**: P < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test
(D), Repstress scores among prostate cancers with different Gleason scores
****: P < 0.0001 by linear trend test from left to right.
(E), Repstress scores and somatic copy number alterations (SCNA) of TCGA prostate cancers SCNA subtype are defined by copy number-based clustering in a previous report (64). ****: P < 0.0001 by linear trend test from left to right.
(F), Repstress scores among uterine corpus endometrial carcinomas with different somatic copy number alteration (SCNA) subtypes
SCNA subtypes are defined by copy number-based clustering in a previous report (65). ****: P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(G), Repstress scores among transcriptomic subtypes in ovarian carcinoma
The molecular subtypes are defined based on transcriptome-based clustering in a previous report (66). ****: P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(H), Repstress scores among genomic subtypes in hepatocellular carcinoma The molecular subtypes (iCluster) are defined based on an integrative analysis of DNA copy number, DNA methylation, mRNA expression, microRNA expression, and reverse phase protein array in a previous report (67). ***: P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(I), Repstress scores between patients with HPV-null (HPV-) and HPV-driven (HPV+) head and neck cancers
****: P < 0.0001 by unpaired Student t test.
(J), (K), (L), Correlations between gene expression of APOBEC3B and repstress score in breast cancer (J), lung adenocarcinoma (K), and acute myeloid leukemia (L)
(M), (N), Repstress score comparison between tumors with KEAP1/STK11 co-alterations compared with those without (M), and tumors with KRAS/STK11 co-alterations compared with KRAS single-altered tumors (N) in lung adenocarcinoma
Gene alterations or copy number deletion (either heterozygous or homozygous) are considered as genetically alteration in KRAS, KEAP1, and STK11. Lung adenocarcinoma with KRAS/TP53 or KRAS/CDKN2A co-mutations are excluded from the analysis in panel (N) given a previous study reporting that non-small cell lung cancer with these co-mutations is different subtype from KRAS/STK11 co-mutated subtype (71,72). ****: P < 0.0001; **: P < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test.
(O), A schema of repstress gene signature characterizing replication stress and its response
Abbreviations: TCGA: The Cancer Genomic Atlas; LumA: luminal A; LumB: luminal B; PDAC: pancreatic adenocarcinoma; AD/SC: adenosquamous; Epi: epithelioid; Sarc: sarcomatoid; GS: Gleason score; SCNA: somatic copy number alteration; CN: copy number; POLE: DNA polymerase epsilon, catalytic subunit; MSI: microsatellite instable; HPV: human papilloma virus; APOBEC: apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like; STK11: Serine/threonine kinase 11; KEAP1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; RS: replication stress; Abbreviations for cancer types in TCGA are available in https://gdc.cancer.gov/resources-tcga-users/tcga-code-tables/tcga-study-abbreviations.
