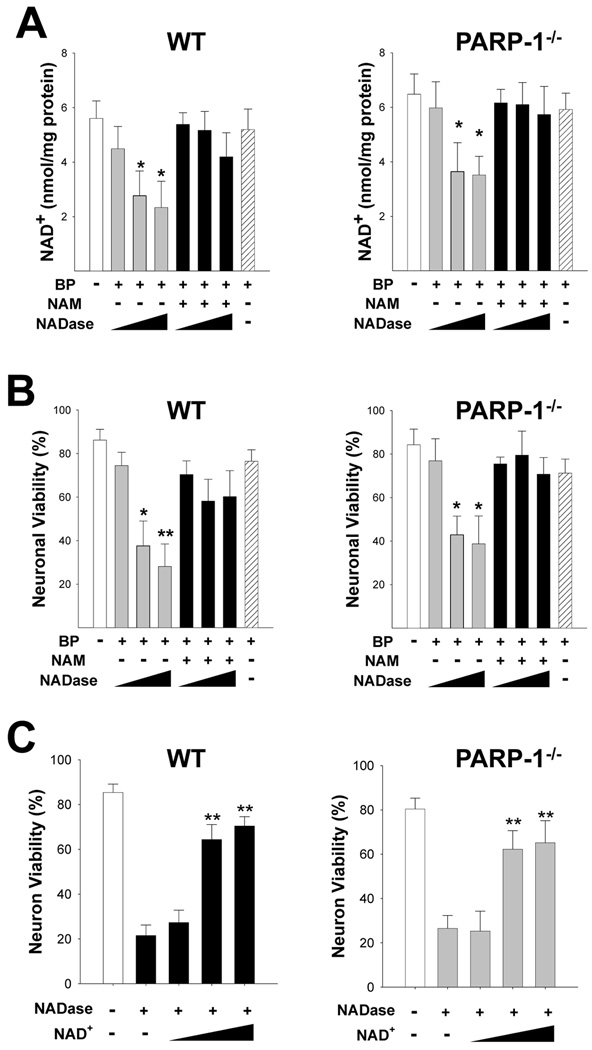
Figure 7. Depletion of cytosolic NAD+ with NADase kills neurons independent of PARP-1 activation.
(A) NADase transfection (10, 30, 100 µg/mL) produced a dose-dependent decrease in neuronal NAD+ content in both wild-type and PARP-1−/− neurons, as measured 3 hours after Bioporter transfection (BP). This decrease was blocked by the NADase inhibitor nicotinamide (NAM, 200 µM) and not observed in cultures treated with the Bioporter vehicle alone (far right bar).
(B) NADase transfection also produced a dose-dependent neuronal death in both wild-type and PARP-1−/− neurons, evaluated 24 hours later. This decrease was blocked by the NADase inhibitor nicotinamide (NAM, 200 µM) and not observed in cultures treated with the Bioporter vehicle alone.
(C) Neuron death due to NADase transfection (30 µg/mL) was significantly prevented by exogenous NAD+ treatment (2.5, 5, and 10 mM) in both wild-type and PARP-1−/− neurons