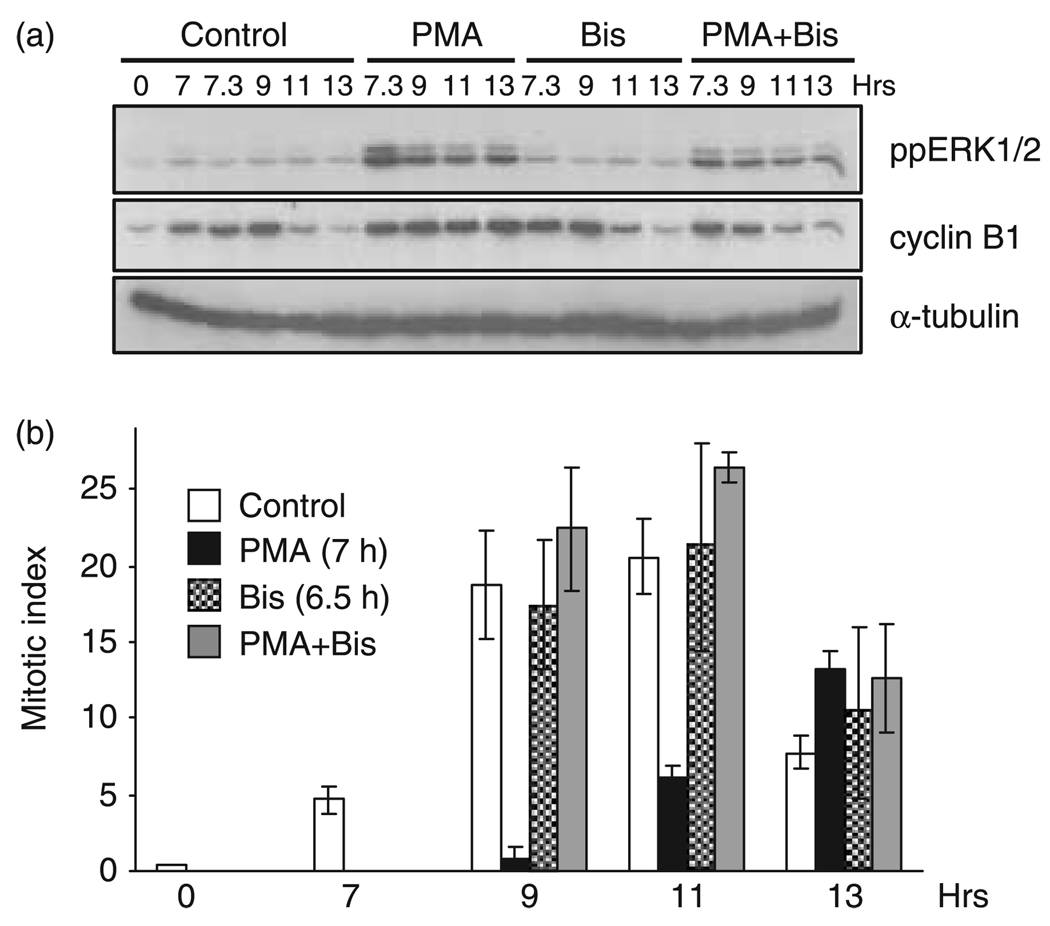
Figure 2. PMA-induced G2-phase arrest requires PKC activity.
Cells synchronized at the G1/S boundary were released back into the cell cycle for 6.5 h and pre-treated with or without Bis (1 µm). At 7 h post-G1/S release, cells were treated in the absence or presence of PMA (0.1 µm) and harvested at the times indicated. (a) Immunoblot analysis of active ERK1/2 (ppERK1/2, top panel) and cyclin B1 (middle panel) as the marker of G2/M progression. The expression of α-tubulin (lower panel) is shown for a protein loading control. (b) The MI at various times after G1/S release in controls (open bars), PMA-treated (black bars), Bis-treated (checkered bars), or Bis- and PMA-treated (grey bars) cells. Data represent the mean and standard error from three independent experiments.