Figure 2: The NVU interaction network.
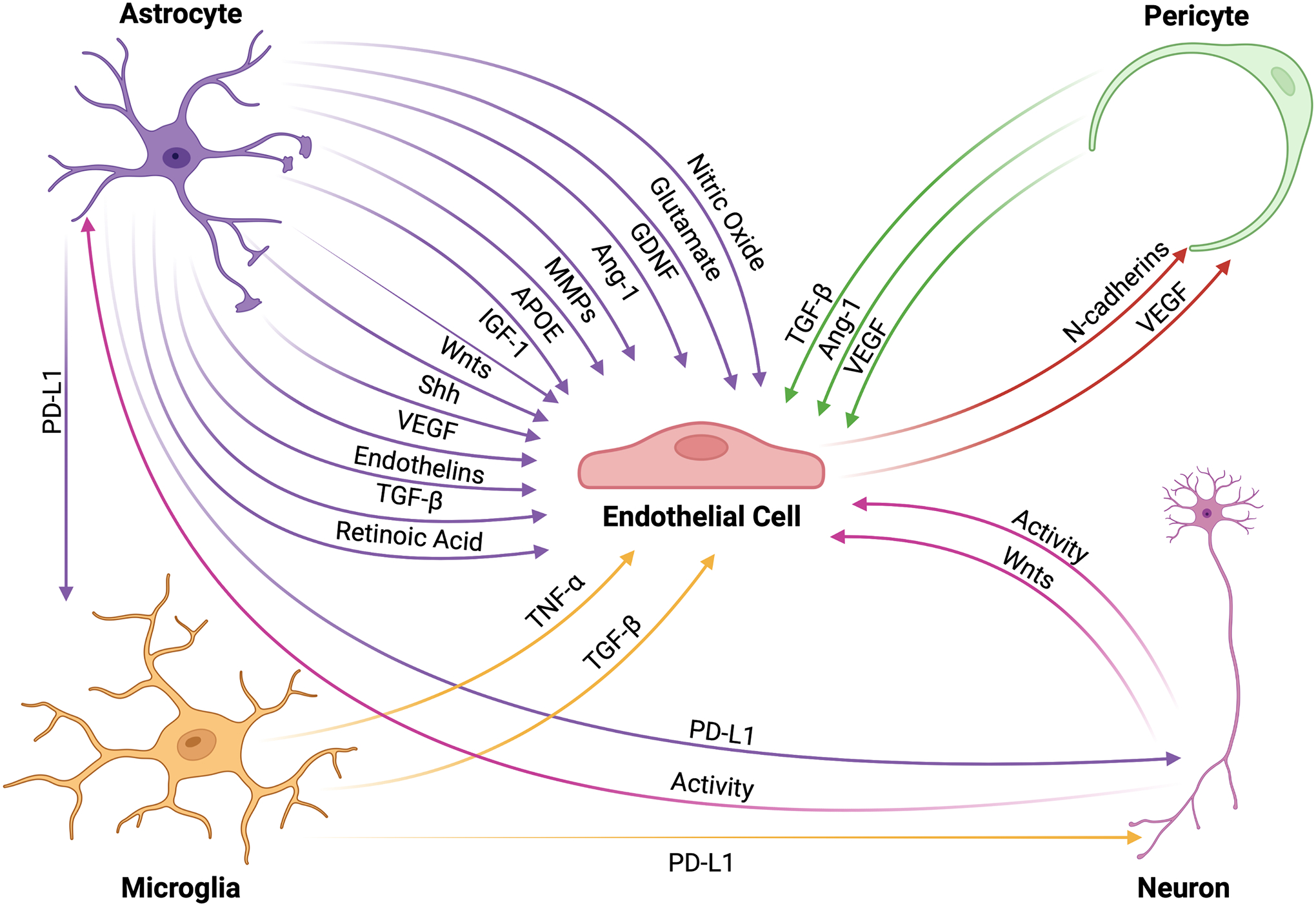
Cells within the NVU interact through intricate signaling mechanisms that allow for proper functioning of the BBB. ECs receive a variety of protective signals from other NVU cells that upregulate tight junction formation thus enhancing BBB integrity. These factors include, but are not limited to, TGFβ, Ang-1, APOE, Shh, Wnts, glial-derived neurotrophic factor, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, and retinoic acid. Contrastingly, ECs may also receive signals that downregulate tight junction proteins, particularly during inflammatory events, such as TNFα, NO, MMPs, endothelins, and glutamate that lead to increased BBB permeability. Importantly, ECs also maintain the ability to signal to pericytes through VEGF and N-cadherin, which are necessary for BBB maintenance. Immune checkpoint proteins, such as the PD-1/PD-L1 complex, regulate the cellular activity of microglia and neurons to modulate BBB integrity as well as dampen the inflammatory activity of infiltrating peripheral immune cells, which increases BBB permeability. Finally, neuronal activity is a critical modulator of cellular and molecular transport across the BBB.
