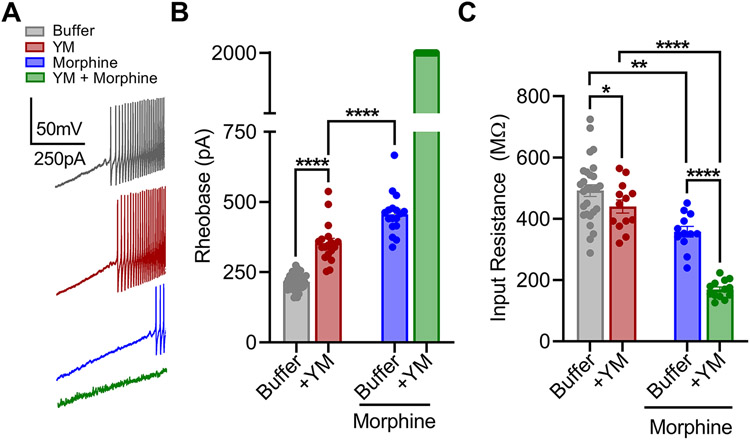
Figure 4: The effect of YM treatment on morphine-provoked inhibition of DRG nociceptors.
A. Representative voltage traces from a continuous 0-2 nA ramp stimulation protocol illustrating excitability of a cultured DRG neuron at baseline (black), after bath application of either 1 μM morphine (blue), or 100 nM YM (maroon) followed by both 100 nM YM + 1 μM morphine (green). B. Quantification of rheobase from DRG recordings illustrated in A. Co-application of YM and morphine prevented action potential firing throughout the 2 nA ramp protocol in all recordings. YM: F(1, 24) = 6032, Morphine: F(1, 24) = 7591, Interaction: F(1, 24) = 4208. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. C. Quantification of resting input resistance at baseline (black), and after bath application of either 1 μM morphine (blue) or 100nM YM (maroon) followed by both 100nM YM + 1 μM morphine (green). YM: F(1, 24) = 6.636, Morphine: F(1, 24) = 172.7, Interaction: F(1, 24) = 57.75. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Statistical analysis was performed combining both sexes, and significance was *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ****p < 0.0001.