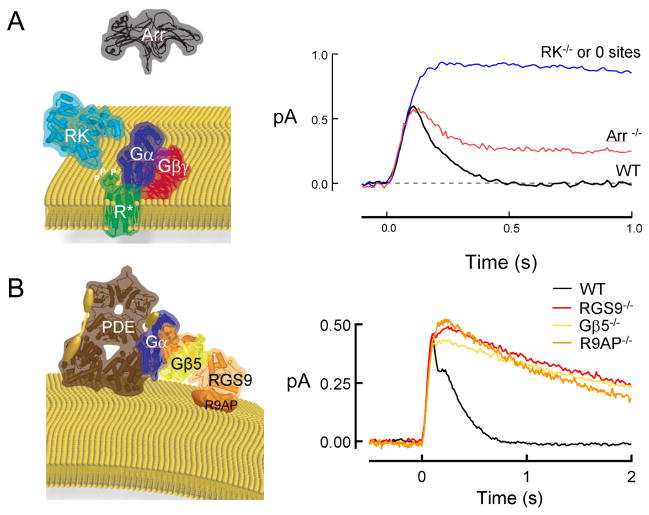
Figure 1.
Deactivation steps essential for normal photoresponse recovery. A. R*deactivation requires phosphorylation by GRK1 (rhodopsin kinase, RK) and the binding of arrestin 1 (ARR1). Traces are population average single photon responses adapted or unpublished from previous studies26, 23, 21, 24. B. Gtα-PDE*deactivation requires GTP hydrolysis that is stimulated by the RGS9 complex consisting of RGS9-1 (RGS9), Gβ5-L (Gβ5), and R9AP. Traces are population average single photon responses adapted or unpublished from previous studies10, 45, 44. Crystal structures of each protein or enzyme exported from RCSBPDB Protein Data Bank (pdb.org) using the Protein Workshop viewer for illustration. PDB Accession numbers were: Rh:2L37, RK:3C50, Arr1:1CF1, RGS9 and Gβ5:2PBI, PDEαβ: 1FL4; Gβ1γ1: 1TBG, Gαt: 1TAD. The representations provided for PDEγ (yellow barbell) and R9AP (orange disc) are cartoons because no crystal structures are yet available.