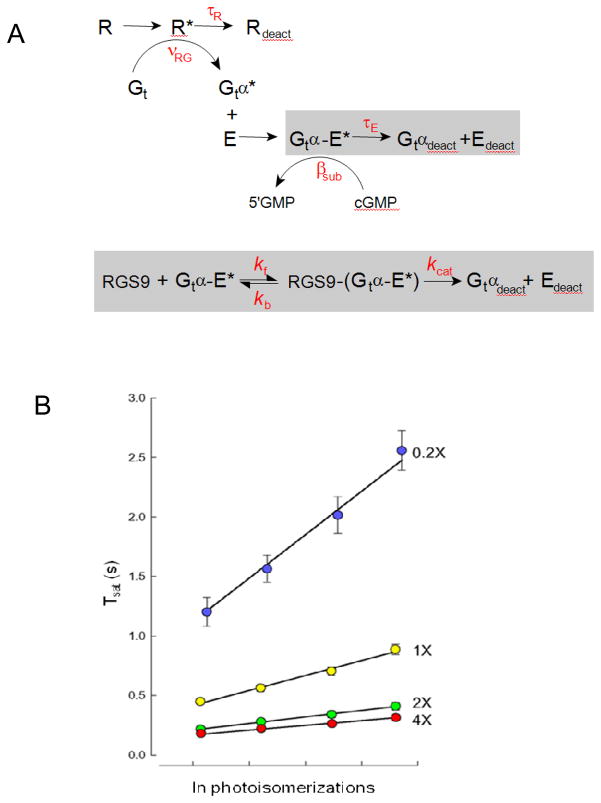
Figure 2.
Michaelis-module for the RGS9-dependence of Gtα-PDE* deactivation reveals the rate constants of RGS9 binding and catalysis, and constrains R* lifetime. A. Standard scheme for phototransduction, in which the Michaelis module for RGS9-mediated GTP hydrolysis (gray box below)was substituted for the first order decay of Gtα-PDE*(gray bow above). B. The time that flash responses remained in saturation (Tsat) as a function of the natural log of the number of R* (photoisomerizations) produced by each flash for mouse rods expressing a 20-fold range of RGS9 complex54. Error bars represent SEMs. Straight lines are the best fitting curves produced using simplex searches of the solutions to the differential equations representing the expanded scheme in A. Parameter values were τR = 33 ms, kf = 0.051 μm2 s−1, kb=13.8 s−1 and kcat=52.8 s−1. Adapted from Burns and Pugh, 200955.