Fig. 1. Identification of broadly neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
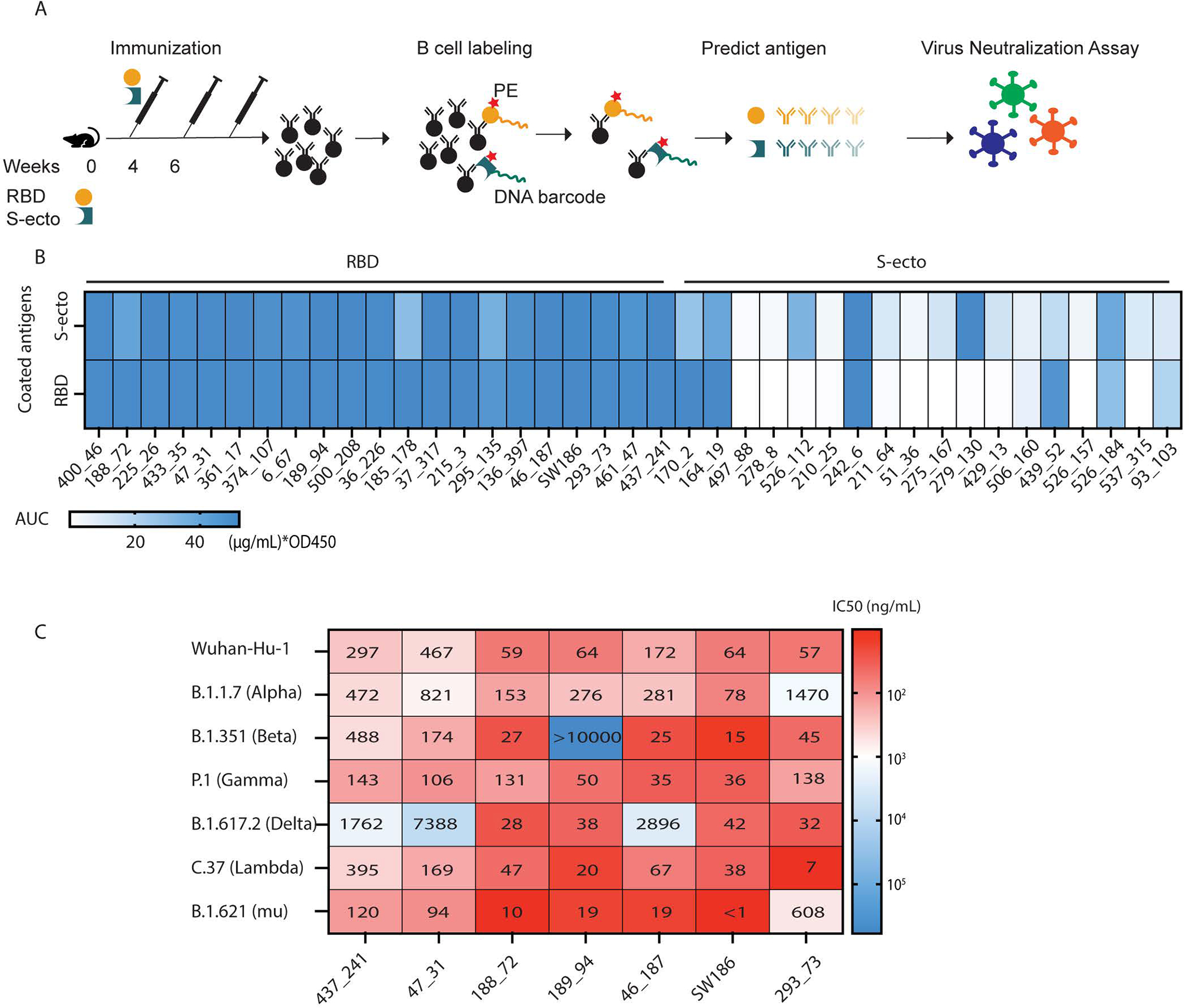
(A) A pipeline of antibody identification and characterization. Splenocytes from mice immunized with the RBD or the ectodomain of spike protein (S-ecto) were stained with biotinylated antigens that were labeled with DNA oligonucleotide barcodes. IgG+ antigen+ cells were sorted and processed for scRNA-seq to obtain the antigen-specific BCR sequences. Each antibody was analyzed by ELISA and neutralization assays using pseudoviruses displaying the spike proteins from SARS-CoV-2 variants. (B) Analyses of antibody binding to the spike protein and RBD. The heatmap shows the area under the curve (AUC) values measured by ELISA assay. The unit of AUC is (μg/mL) * OD450. The y-axis indicates the antigens used to coat the ELISA plates, and the labels on the top indicate the antigens used to immunize the mice. (C) IC50 values from the neutralization assays of seven selected antibodies using pseudotyped viruses displaying the spike proteins from indicated SARS-CoV-2 variants. The heatmap shows the −log(IC50), and the numbers in the plot represent the IC50 values in ng/mL (representative data from three independent experiments).
