Fig. 3. Structural analysis of SW186 Fab bound to RBD-SD1.
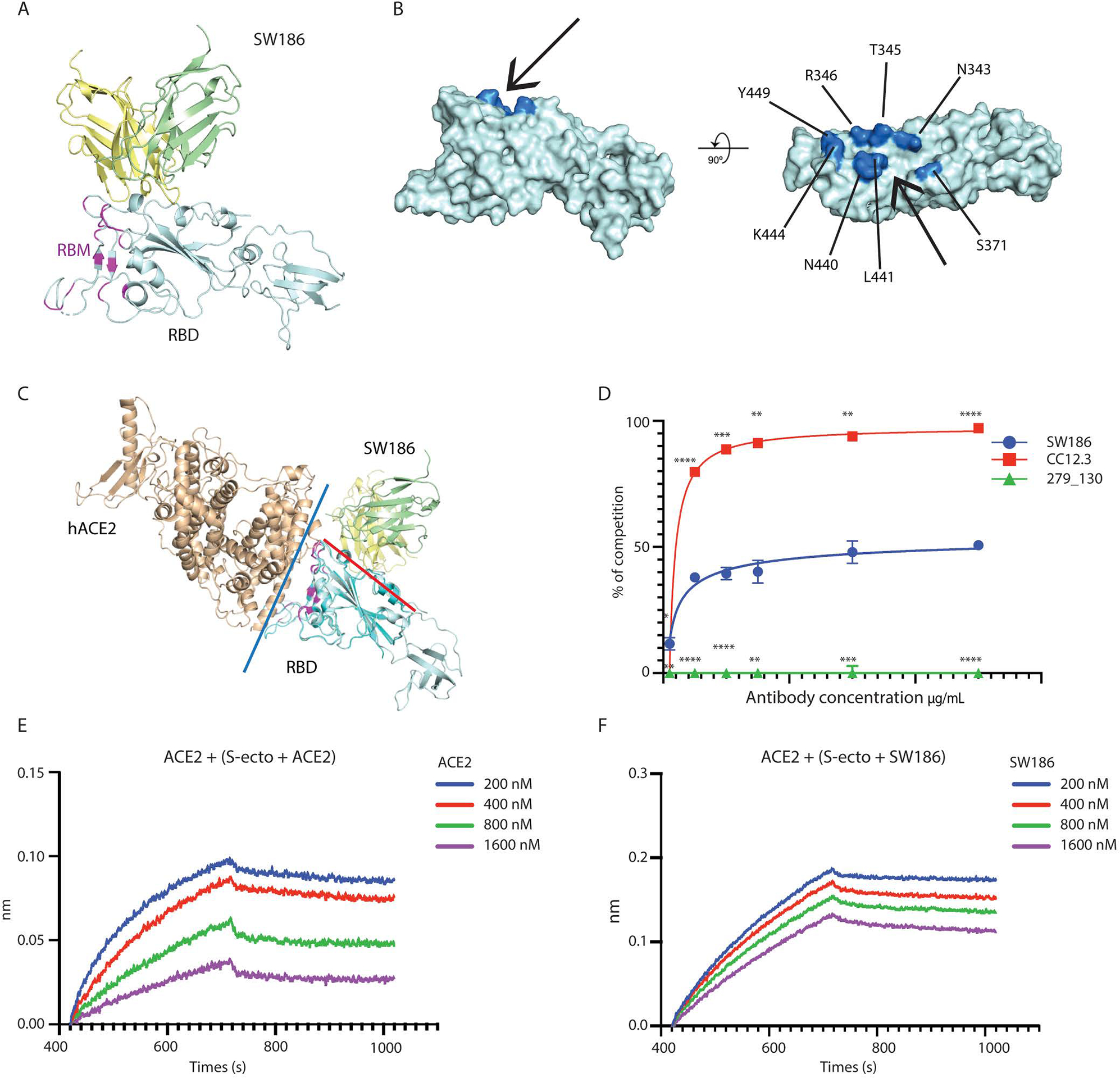
(A) Overview of the locally refined structure of SW186 Fab bound to spike-RBD-SD1. Variable regions of the heavy chain (VH), light chain (VL), and RBD-SD1 are colored pale yellow, pale green, and pale cyan, respectively; receptor-binding motif (RBM) of the spike protein is colored magenta. (B) Surface presentation of RBD binding epitope of SW186. Critical residues on RBD are colored marine. The ‘minor groove’ is shown with an arrow. (C) Superposition of SW186 Fab bound to RBD-SD1 and hACE2 bound to RBD (PDB code: 6M17). hACE2 and RBD are colored wheat and cyan, respectively. Variable regions of the heavy chain (VH) and light chain (VL) are colored pale yellow and pale green, respectively. Red and blue lines show the interfaces between SW186 Fab and RBD and between hACE2 and RBD, respectively. The spike RBM is colored magenta. (D) Cell-based assay of the spike protein binding to ACE2 and competition by the antibody. Each data point represents triplicates. Two-way ANOVA was used to assess the significance of difference. * indicates statistical difference of the indicated antibody as compared to SW186. p-values: ≤ 0.05 (*), ≤ 0.01 (**), ≤ 0.001 (***), ≤ 0.0001 (****). (E-F) Kinetics of competitive binding of antibody SW186 and hACE2 to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. For both panels, biotinylated hACE2-Fc was loaded onto the streptavidin sensor. S-ecto protein was pre-incubated with serially diluted ACE2-His6 (E; as a positive control) or SW186 (F) for 30 min at RT. The mixture was further loaded onto the hACE2-Fc coated sensor to detect the binding of S-ecto to ACE2.
