Fig. 5. SW186 protects mice from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
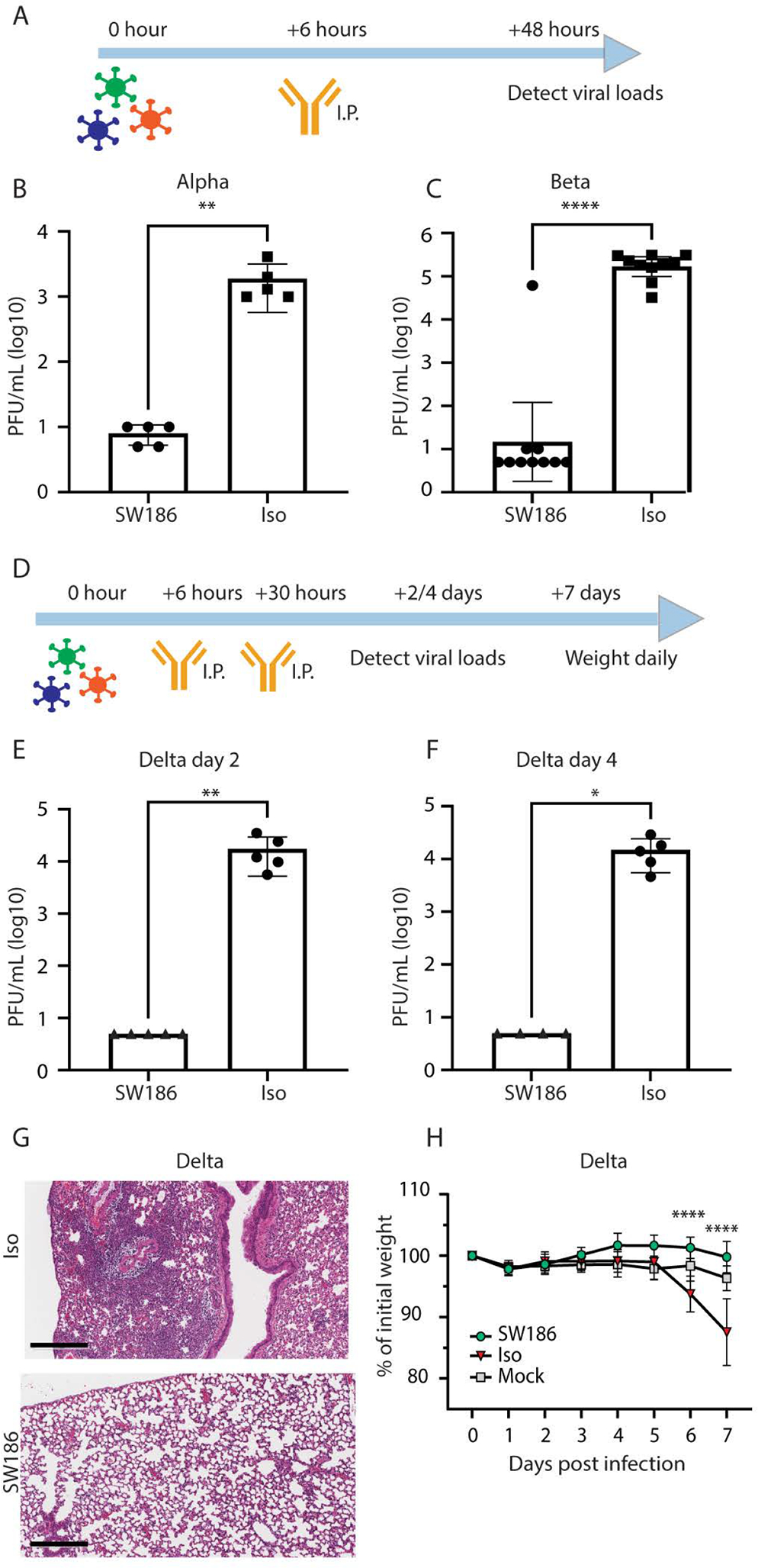
(A) The schematics of antibody treatment in mice infected with the Alpha and Beta variants of SARS-CoV-2. Mice were intranasally infected with the indicated SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. After 6 hours, the SW186 antibody or its isotype control antibody (Iso) was intraperitoneally (I.P) injected into mice. Lungs were harvested 2 days after infection to measure the viral loads. (B) Viral loads measured by plaque assay on day 2 post SARS-CoV-2 Alpha infection (n = 5). Antibody dose: 2.8 mg/kg. (C) Viral loads measured by plaque assay on day 2 after SARS-CoV-2 Beta infection (n = 10). Antibody dose: 5 mg/kg. (D) The schematics of antibody treatment in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 Delta virus. Human ACE2 transgenic mice were intraperitoneally injected with SW186 or its isotype control (3 mg/kg) at 6 hours and 30 hours after viral infection. (E-F) Viral loads were measured by plaque assay on day 2 (E) and day 4 (F) after SARS-CoV-2 Delta infection (n = 5). Mann Whitney test was used in A-F. (G) Histopathology analysis of lungs from SARS-CoV-2 Delta infected mice. Lungs harvested at 4 days post-infection were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Scale bars, 300 μm. Representative images from five mice per group. (H) Mouse body weights were measured daily after SARS-CoV-2 Delta infection and antibody treatment. N=5 for each antibody-treated group; Mock: no virus infection, n = 10. Statistical significance was tested by two-way ANOVA. p-values: ≤ 0.05 (*), ≤ 0.01 (**), ≤ 0.001 (***), ≤ 0.0001 (****).
