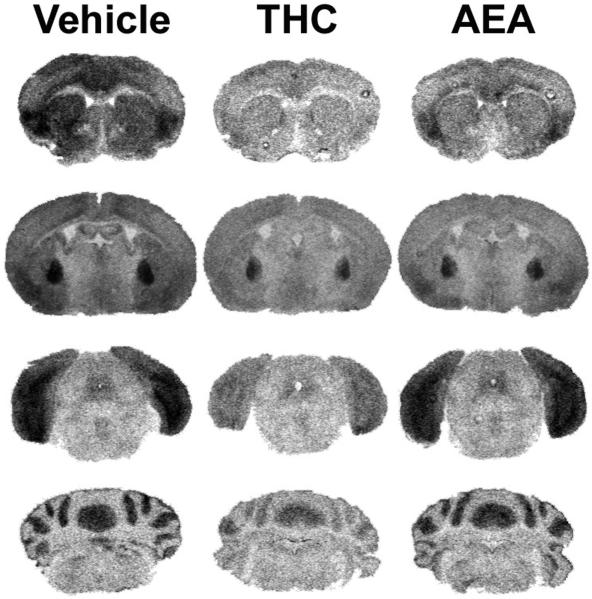
Figure 6.
Representative autoradiograms illustrating WIN55,212-2 stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in brains from vehicle, THC- and AEA-treated FAAH−/− mice. WIN55,212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding is visibly reduced in FAAH−/− mice treated with THC in nearly all regions including caudate-putamen (top panels), globus pallidus (top center panels), PAG (bottom center panels), and cerebellum (bottom panels). AEA-treated FAAH−/− mice had intermediate levels of WIN55,212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding between vehicle and THC-treated mice. Data from densitometric analysis are presented in Table 4.