Figure 1: Ribociclib is brain penetrant and decreases pRB, Ki67 and the expression of E2F target genes in human and mouse G3MB tumors.
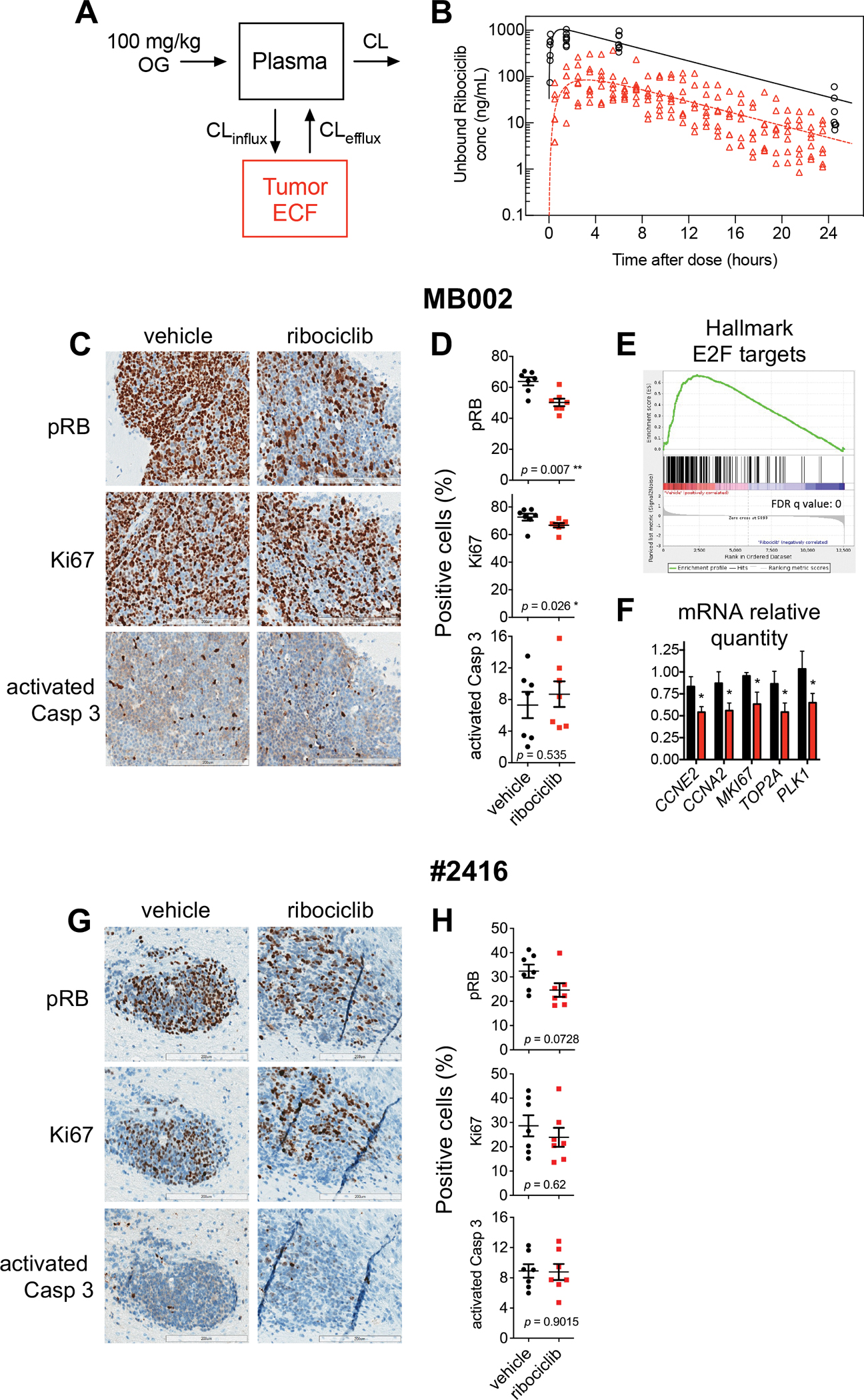
(A) Ribociclib plasma and extracellular fluid (ECF) model predictions in the mouse G3MB tumor #2416. (B) Pharmacokinetic model structure. Unbound plasma concentrations (open black circles), mean model plasma predictions (solid black line), in tumor ECF concentrations (tECF, open red triangles), and mean model tECF predictions (dashed red line) in the mouse G3MB tumor #2416. CL, CL influx, CL efflux represents the elimination plasma to ECF influx and efflux clearances. OG = oral gavage. CL= clearance. Mice bearing human PDOX MB002 (C-F) or mouse tumor #2416 (G-H) tumors treated with vehicle or ribociclib (100mg/kg), daily for 5 days and euthanized 4h post last dose. (C, G) Representative immunohistochemistry images tumors stained with antibodies against pRbSer807/811 (pRB), Ki67 and activated Caspase-3. (D, H) Quantification of the percentage of positive cells for each staining (Mann-Whitney test, n=7 per group for MB002 (D) and #2416, (H), p ≤ 0.05 (*), p ≤ 0.01 (**)). Note: two untreated #2416 tumors added to #2416 vehicle group (H). (E) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) showed significant depletion of HALLMARK_E2F_TARGETS in ribociclib versus vehicle treated MB002 tumors. (F) Relative mRNA level of selected E2F target genes quantified by qRT-PCR (Mann-Whitney test; n=4 per group; p ≤ 0.05 (*)).
