Figure 5.
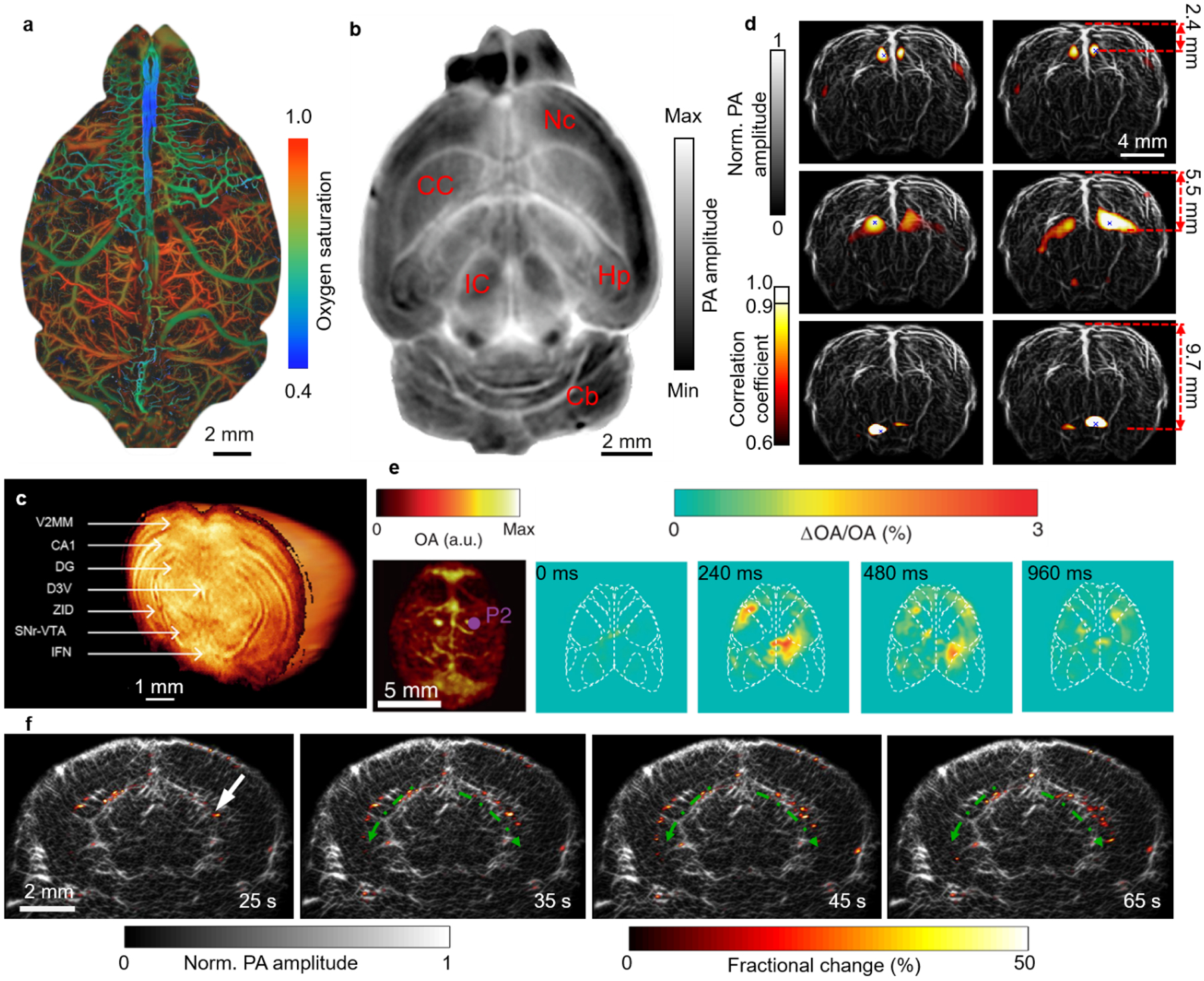
Multiscale PAT of the brain. (a) PAM of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in a mouse brain.79 (b) A cross-sectional PACT image of a saline-perfused mouse brain (horizontal plane) at 2.8-mm depth, showing internal structures of the brain clearly. Nc, neocortex; CC, corpus callosum; Hp, hippocampus; Cb, cerebellum; IC, inferior colliculus.80 (c) 3D PACT image of a mouse brain ex vivo. Illumination wavelength, 740 nm; V2MM, secondary visual cortex, medio-medial; CA1, hippocampal CA1 area; DG, dentate gyrus; D3V, dorsal third ventricle; ZID, zona incerta dorsal; SNr, substantia nigra reticulate; VTA, ventral tegmental area; IFN, inter-fascicular nucleus.81 (d) Functional mapping of the resting-state connectivity in a rat whole brain (coronal plane), showing a clear correlation between corresponding regions across the left and right hemispheres.58 (e) PACT of GCaMP6s responses to electrical stimulation of the right or left hind paw. First from the left, maximum amplitude projection along the depth direction of the 3D images of a GCaMP6s-expressing mouse; second to last, relative increases in PA signal with respect to the baseline for a slice at ~1 mm depth at different time points following the stimulation pulse for the GCaMP6s-expressing mouse.82 (f) PACT images of epileptic activities during a seizure at different times. The fractional changes (color) in the PA amplitude are overlaid on the anatomical image (gray, Bregma −1.0 mm). The arrow indicates the injection site, and the dashed green arrows indicate the epileptic wave propagation direction.83
