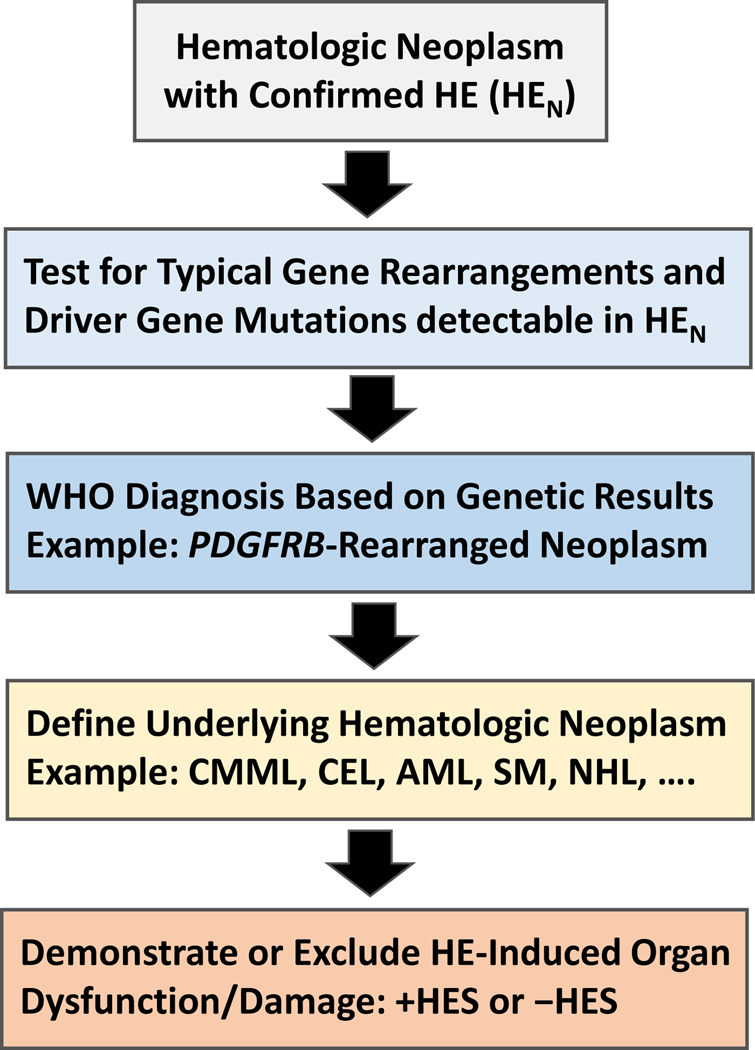
Figure 2.
Diagnostic algorithm for patients suffering from hematologic diseases accompanied by clonal/neoplastic hypereosinophilia (HEN)
In a first step, the presence of HE must be confirmed by measuring blood counts and the percentage of eosinophils by microscopy. In a next step, leukocytes are examined by PCR and next generation sequencing for the expression of certain gene variants known to be present in myeloid and stem cell neoplasms associated with HE. In addition, leukocytes from the bone marrow or blood are examined for specific abnormalities by conventional karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). At the same time the underlying stem cell or myeloid neoplasm is defined by detailed studies of bone marrow and blood cells, including histomorphological, immunohistochemical, immunological, and biochemical analyses. When the patient is suffering from a lymphoid neoplasm (NHL), HE is considered to be non-clonal and the diagnosis usually changes to HER. In a final step, the patient is examined for the presence of signs and symptoms of specific organ involvement that could qualify as HE syndrome (HES). Here it is of utmost importance to explore the case history and to ask the patient about previous potential HES-related events, such as a thromboembolic complications. Abbreviations: HE, hypereosinophilia; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; CMML, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; CEL, chronic eosinophilic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; SM, systemic mastocytosis; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; NHL, Non Hodgkin lymphoma; +HES, with concomitant hypereosinophilic syndrome; -HES, without HES.