Figure 2. Effects of intrarenal artery infusions of inosine and guanosine on renal excretory function.
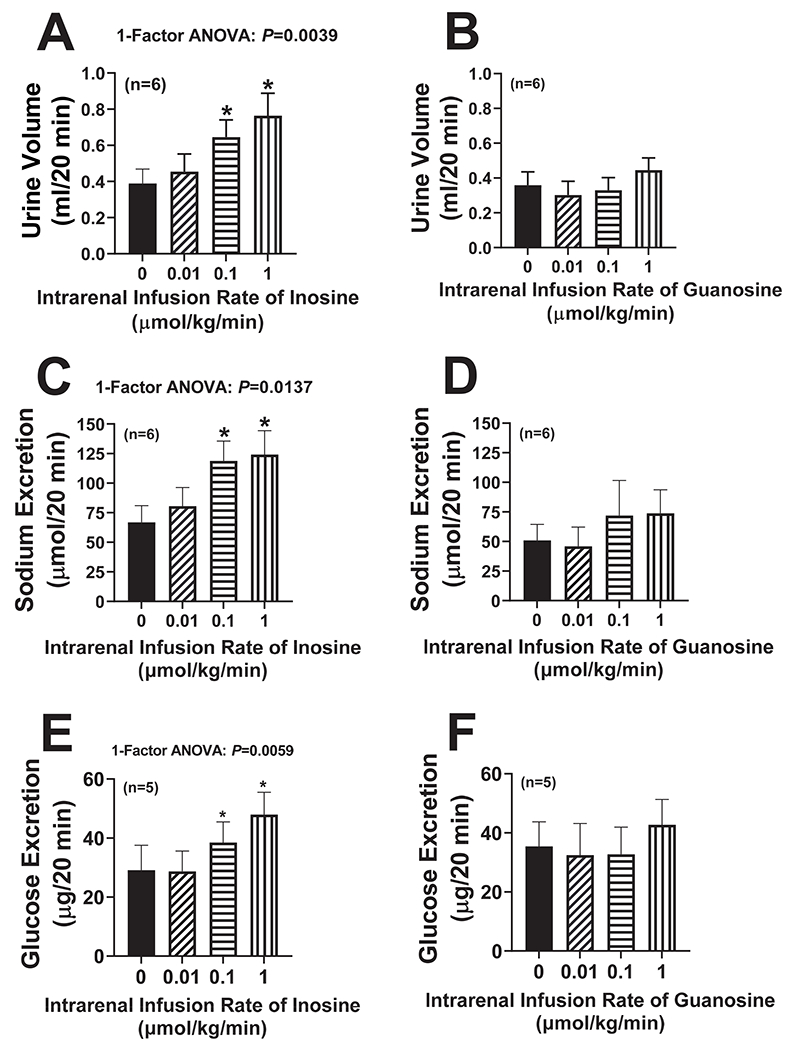
Inosine (A,C,E) or guanosine (B,D,F) was infused directly into the renal artery of anesthetized rats at increasing doses [0 (vehicle only; basal), 0.01, 0.1 and 1 μmol/kg/min]. Each dose of inosine or guanosine was administered for 30 min, timed collections of urine were obtained from the ureter between 10 and 30 min after initiating a given dose of inosine or guanosine, and urine volumes (A,B) and excretion rates of sodium (C,D) and glucose (E,F) were determined. Values are means and SEMs for the indicated sample size (n). ANOVA, analysis of variance; *P<0.05 vs 0 (vehicle; basal).
