Figure 3.
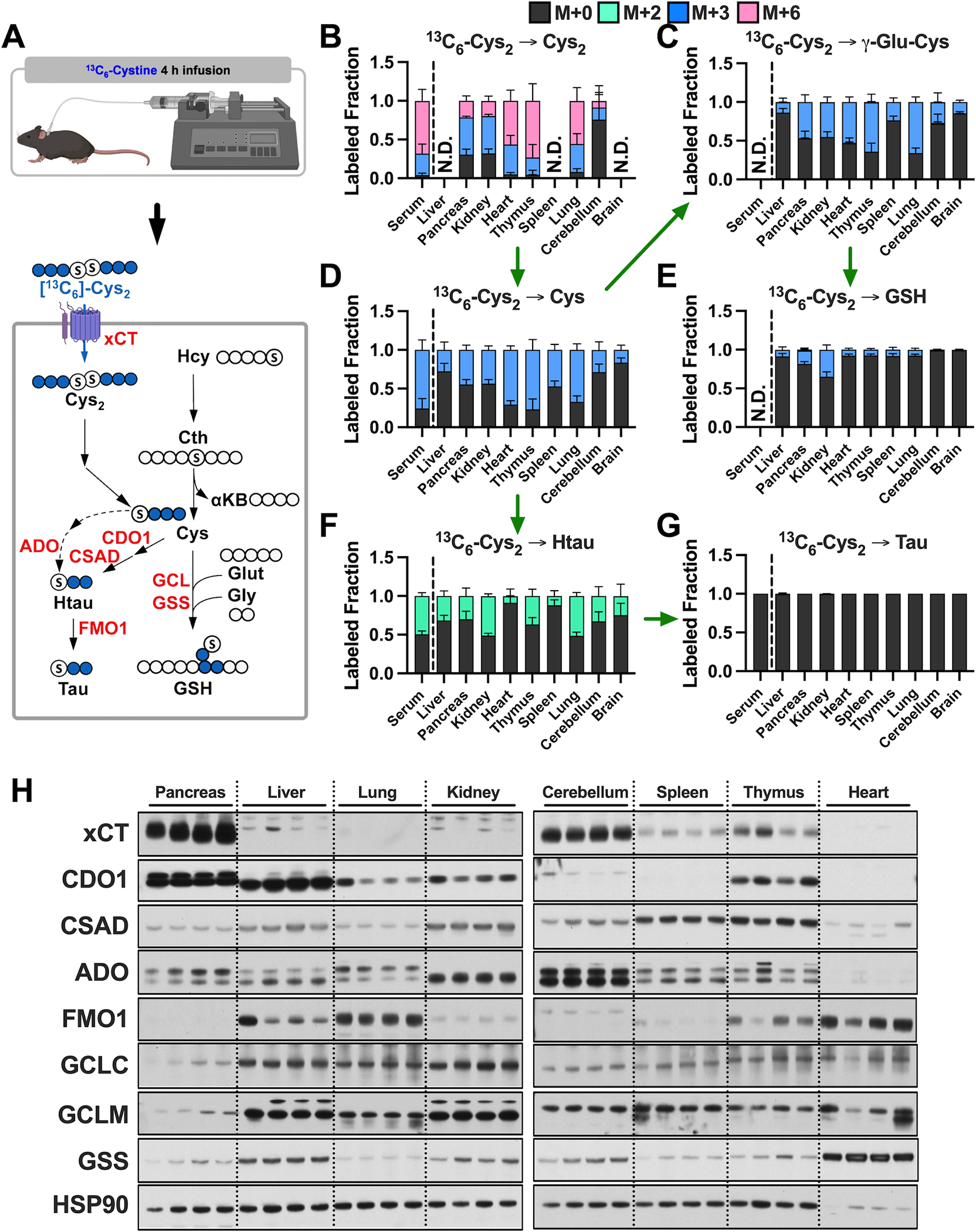
Cyst(e)ine supplies the cysteine pool in all tissues. A, Schematic depicting 13C6-cystine infusion and its metabolism to glutathione and taurine. Created in part with Biorender.com. B-G, Healthy C57BL/6J mice were infused with 13C6-cystine, followed by analysis of the fraction labeling in B cystine, C γ-glutamylcysteine, D cysteine, E glutathione, F hypotaurine and G taurine. For B-G, data are presented as mean ± SD and N=5 mice. N.D., not detected. H, Immunoblots of cystine/glutamate antiporter (xCT), cysteine dioxygenase type 1 (CDO1), cysteine sulfinate decarboxylase (CSAD), 2-aminoethanethiol (cysteamine) dioxygenase (ADO), flavin-containing monooxygenase 1 (FMO1), glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM), and glutathione synthetase (GSS) for each tissue. HSP90 is used for the loading control. Cys2, cystine; Hcy, homocysteine; Cth, cystathionine; aKB, α-ketobutyrate; Cys, cysteine; Gly, glycine; Glut, glutamate; GSH, glutathione; γ-Glu-Cys, γ-glutamylcysteine; Htau, hypotaurine; Tau, taurine
